Material calculation
| TOTAL: on the walls | 365208 rub. |
| FOUNDATION: | |
| gravel bedding: | |
| 11.8 m³ x 1900 rub/m³ | 22420 rub. |
| concrete mix B15-20: | |
| 9 m³ x 4200 rub/m³ | 37800 rub. |
| concrete mix B15-20: | |
| 39 m³ x 4200 rubles/m³ | 163800 rub. |
| reinforcing bars Ø10, 12, 16 AIII: | |
| 3.1 t x 37500 rub/ton | 116250 rub. |
| foundation blocks FBS 24-3-6: | |
| 57 pcs. x 2360 rub./pc. | 134520 rub. |
| sand-cement mix: | |
| 1.5 m³ x 2700 rub/m³ | 4050 rub. |
| edged boards for formwork: | |
| 1.7 m³ x 6500 rub/m³ | 11050 rub. |
| roll waterproofing RKK-350: | |
| 4 rolls x 315 rubles/roll (10m²) | 1260 rub. |
| TOTAL: on the foundation | 491150 rub. |
| COVERS: | |
| wooden beams 150x100: | |
| 4.8 m³ x 7000 rub/m³ | 33600 rub. |
| drywall Knauf (2500x1200x10): | |
| 29 pcs. x 260 rub./pc. | 7540 rub. |
| steel profile with fasteners: | |
| 247.1 l.m x 50 rub./l.m | 12355 rub. |
| mineral wool insulation (Rockwool): | |
| 21.3 m³ x 3700 rub/m³ | 78810 rub. |
| waterproofing (Tyvek Soft): | |
| 205 m² x 68 rubles/m² | 13940 rub. |
| PE vapor barrier: | |
| 205 m² x 11 rubles/m² | 2255 rub. |
| plywood sheets FK 1525x1525x18: | |
| 1.5 m³ x 19000 rub/m³ | 28500 rub. |
| subfloor edged boards: | |
| 1.7 m³ x 6500 rub/m³ | 11050 rub. |
| TOTAL: by floors | 188050 rub. |
| ROOF: | |
| pine racks (150x50mm): | |
| 4 m³ x 7000 rub/m³ | 28000 rub. |
| antiseptic composition: | |
| 59 l x 75 rubles/liter | 4425 rub. |
| waterproofing (Tyvek Soft): | |
| 184 m² x 68 rubles/m² | 12512 rub. |
| onduline corrugated sheet 2000х950х2.7: | |
| 106 sheets x 399 rubles/sheet | 42294 rub. |
| roofing nails 73x3mm: | |
| 23 pack. x 190 rubles / pack (250 pcs.) | 4370 rub. |
| figure skate (1000mm): | |
| 13 pcs. x 290 rub./pc. | 3770 rub. |
| edged boards 100x25mm: | |
| 1.5 m³ x 7000 rub/m³ | 10500 rub. |
10:0,0,0,290;0,290,290,290;290,290,290,0;290,0,0,0|5:100,100,0,290;195,195,0,290;0,100,100,100;100,195,139,139;195,290,100,100|1127:139,139|1327:75,37;75,109|1527:195,37;195,109|2244:0,33;0,172;290,172|2144:34,0;34,290;129,290;224,290|2417:290,34;290,67|2317:169,0|1927:132,-20
RUB 1,244,599.0
Only for the Moscow region!
Calculation of the cost of work
Do you want to know how much it costs to build your house and choose contractors?
Place an express application and get offers from professional builders!
Layout example 10x10 m for calculation |
Structural scheme |
|
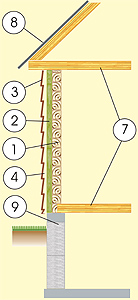 |
1.
Wooden bars150x150mm; 2. cladding with siding; 3. slab mineral insulation d=100mm; 4. Ventilation channel d=20-50mm; 7. Wood beam ceilings d=150-250mm; 8. Ondulin sheets; 9. Foundation from a monolithic concrete slab and prefabricated blocks h = 1.8m; |
|
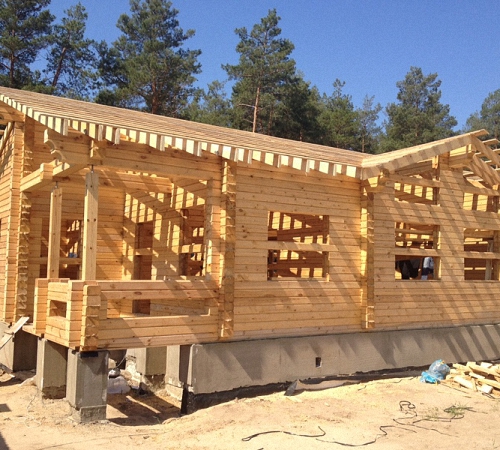
Wall made of timber material with siding profile trim and internal heat insulator

timber wall
The features of wooden-beam housing have been proven to neutralize toxic substances, automatically adjust the amount of humidity in the range of 45-55%, and also have a beneficial effect on the psyche of residents.The popularity of wooden-log architecture in our country is predetermined by the economy, tradition and healthy environment of housing construction from a natural array.
At construction bases, it is possible to find lumber products of sizes 150x100, 200x150, 100x100, 140x140, 180x180, 150x150, 120x120, of which the 150x150 type is the most purchased, as it provides the optimal combination of installation labor intensity, given by the number of horizontal seams, and thermal insulation qualities , and also affordable price.
It should be added that now the share of sales of profiled, in particular, prefabricated glued timber, is clearly growing, which is characterized, in comparison with non-glued wood, by 10 times lower compressibility during drying, as well as increased, due to studded joints, structural and thermal insulation qualities . An obvious negative point that slows down the widespread use of glued laminated lumber is its significant cost, which, however, is compensated a hundredfold by its long service life.
An approximate procedure for laying a log cabin:
- First, on the top of the foundation, covered with waterproof material, along the line of the walls, the lower beam row is laid out, which is tied "in the paw" at the corners and at the points of attachment of the intermediate walls.
- To prevent door and window structures from deforming during shrinkage wooden house, door and window niches are surrounded on the sides with a "pigtail" - racks-profiles. To do this, a trapezoidal spike is cut out at the ends of the logs, onto which, with the help of a reciprocal cutout, the named profiled bars are pushed. At the top of doors and windows, technological slots are arranged, laid with flax-jute or basalt insulation.
- During the installation of the log house, the log rows are covered with an inter-row compactor: felt, jute, flax jute, hemp, flax, tow, which a year later (or when the moisture content of the tree becomes 12-15 percent) will have to be re-compacted a second time in order to reduce heat loss through the gaps between logs.
- In order to connect the beams of the near crowns, dowel fastening is used (rounded birch or oak rods with a diameter of Ø30-40 mm), which are inserted with a gap into holes made through three crowns of the beams, in increments of 0.3 ... 0.4 m. Often, the dowel fastening is replaced with large nails (250 ... 300 mm), with obligatory drilling in the last log of the channel, 30 ÷ 40 mm deep, where the nail head is buried, to compensate for linear compression wooden material when dry.
- When choosing interior finishes, one should take into account the permanent deformations of the wooden material and, when fixing non-wooden facing boards (for example, drywall), avoid direct connections to the timber wall, by means of suspended buffer profile structures.

siding cladding
In the case when winter habitation is expected, it is recommended that the timber structure is also thermally insulated. Usually, on the street side, in a vertical position, thick boards are mounted, 100x50 mm in size, with a step of 0.4 ... -125, PPZh-200, Ursa, Knauf, Izorok, after that a vapor-permeable film (Tyvek, Yutavek, Izospan) is stretched, lined with blocks, 25-50 mm thick, along which the front false wall is installed (PVC siding, wooden lining or slabs CSP).
You need to know that PVC siding profile will be used for many years and have a beautiful appearance, only under the condition of strict observance of the installation rules.
Manufacturers of plastic siding profiles, such as Snowbird, Gentek, Docke, Nordside, AltaProfile, Ortho, Holzplast, Tecos, Varitek, Georgia Pacific, Mitten, FineBer, Vytec, announce a rich color scheme that allows any building to retain its individuality.
Since the PVC siding profile changes linear dimensions very much with temperature fluctuations, it is important to provide for non-rigid attachment of vinyl plates.
Polyvinyl chloride siding does not rot, is resistant to shock, biological, climatic aggression, does not support combustion.
The vinyl profile under the influence of an open flame only melts, igniting when heated to more than 390 ° C (moreover, wood is already at 230-260 ° C), quickly extinguishing when the heating source disappears, while the amount of emissions hazardous to health is no more significant than during the combustion of materials from wood.
Important points for fixing PVC siding:
- Installation of PVC panels is carried out "from the ground", and, at first, a hidden initial strip is fixed.
- To compensate for free compressions or expansions of polymer siding, slots should be provided, within 1 cm, in the input areas of external networks (pipes, wires, brackets, cables), as well as in docking areas plastic panel and accessories (outer corner, inner corner, H-profile, trim, etc.).
- It is unacceptable to tighten the self-tapping screws with force in the fixing grooves, because the siding profiles are suspended in such a way as to move freely from side to side.
- In order not to interfere with thermal shifts and, accordingly, not to provoke wave-like warping of the vinyl material, it is more correct to screw in self-tapping screws and nail nails into the siding panel to the central point of the existing technological perforations.
- When hanging the next strip of siding, dock it behind the trailing ledge with the underlying profile and, without deforming, fix it with screws;
- It is recommended to install vinyl profiles starting from the side wall of the building, moving to the front side, while each next siding panel will overlap the previous one in the stacked row, approximately 2.5-3 cm - this approach makes it possible to make inconspicuous joints, with for the same purpose, the arising joints, for connecting rows, must be shifted horizontally.
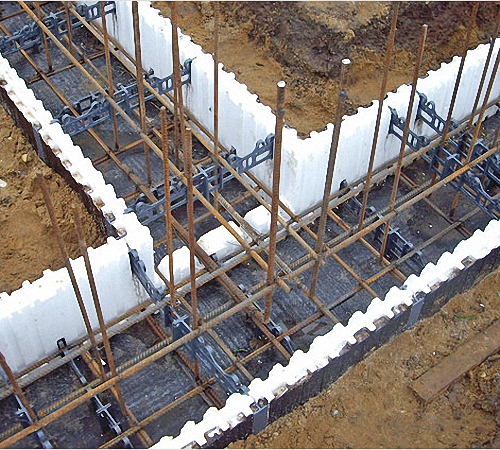
Foundation made of reinforced concrete slab and prefabricated block tape

The prefabricated slab foundation is constructed over the entire area of the structure in the form of a solid reinforced slab, on which standard reinforced concrete blocks are mounted.
The considered type of foundation is used in low-rise housing construction to obtain the basement level of the house, on heterogeneous soils, in a situation of low groundwater levels. On swampy areas, it is recommended to carry out the side walls of the foundation using a monolithic method, using waterproof measures (coating, impregnation, gluing).
At the same time, the prefabricated block system of vertical walls of the foundation, according to the existing reinforced concrete slab, is indispensable with limited construction time, as well as in the production of foundation work in the winter.
An exemplary methodology for performing an integral slab foundation side walls in the form of a prefabricated reinforced concrete tape:
- At the beginning, the land is removed to the planned mark.
- Gravel preparation is poured onto the resulting sub-base, fractions 20-40, with a layer of 15-20 cm, and carefully compacted.
- Concrete pouring is carried out, with a layer of 50 mm.
- A waterproofing film is applied with an offset of 2000 mm along the border, in order to further waterproof the foundation sidewalls.
- For protection waterproofing membrane from accidental ruptures during welding of the reinforcing structure, another layer of sand-cement mortar, 5 cm thick, is applied over the insulating coating, along the perimeter of which formwork panels are mounted along the thickness of the foundation slab.
- The foundation slab being made is pulled together from the inside with two meshes of welded reinforcing bars of section d14 of type AII-AIII with cells of 20x20 cm.
- In the case of a slab foundation, ready-made concrete is required, grades not lower than M300, supplied by an automixer.
- The period of hardening of the concrete mortar, when the perimeter of ready-made concrete blocks should be laid out, is from 4 weeks, at a temperature of + 15 ± 5 °.
- Concrete blocks are laid relative to the center lines, along two mutually perpendicular walls, guided by geodetic equipment. Prefabricated blocks are laid with a crane on a "bed" of sand-cement mortar.
- The installation begins with the laying of lighthouse blocks at the crosshairs of the axes and at the corners of the building. The laying of wall blocks is started only after the alignment of the position of the landmark blocks along the horizon and level.
- On the top row of reinforced concrete blocks, in a panel formwork form, a reinforced reinforced concrete screed is made, 25 cm thick.
Covering from wooden beams

For beam ceilings, coniferous wood (spruce, pine, larch) with a moisture content of less than 14 percent is traditionally used. The best beam is a bar with sectional proportions of 7/5 (for example, 0.14x0.10 m).
In suburban construction, floors made of wooden beams are especially common, due to the simplicity and low cost of their construction.
When planning a timber-and-beam floor, it is necessary to use special diagrams that determine the correlation of the dimensions of the beam from the distance between the supports and the load; it is also permissible to build on the simplified calculation that the wide side of the beam should be approximately 1/24 of the beam length, and the thickness should be 5 ÷ 10 cm, with intervals between beam boards of 50 - 100 cm and a load of 1.5 kPa.
With a deficit of a lag of the calculated section, it is permissible to use boards tightened with bolts, subject to the obligatory observance of the total size.
Some features of the installation of wood beams:
- The installation of beams is done in the following order: first, the first and last, and then, with leveling at the optical level, all the others. The bars should be wound onto the wall structure no shorter than 150-200 mm.
- The logs are moved away from the wall by at least 50 mm, and the distance between the beams and the smoke channel must be at least 0.40 m.
- in wooden buildings, the ends of the lag are hemmed in the shape of a cone, and then they are hammered into the completed drank of the upper crown to the full thickness of the wall log.
- As a rule, in brick walls, the ends of the beams are installed in masonry nests, in which condensate appears, therefore, between the cut ends of the log and the wall, they leave space for air circulation, and with a significant depth of the opening, an additional felt layer is placed.
- To avoid mold, which occurs when steam diffuses into the environment brick wall, the ends of the beam boards are cut with an inclination of about 60 degrees, treated with an antiseptic (Tikkurila, Kartocide, Dulux, Biofa, Pinotex, Tex, Cofadex, Biosept, KSD, Holzplast, Senezh, Teknos, Aquatex) and covered with roofing paper, leaving the end open.
The attic floor is insulated with the implementation of a vapor barrier layer under the insulation, the basement floor is thermally insulated with the installation of a vapor barrier film on top of the insulation layer, and the interfloor ceiling is not subject to insulation.
If the question of the load capacity of wooden floors is mainly settled by the method of an obvious increase in the cross section of the beams and their number, then the situation with fire resistance and acoustic insulation is somewhat more complicated.
One of the options for improving the soundproof and fireproof performance of timber interlevel ceilings consists of the following steps:
- To the bottom of the beam beams, perpendicular to them, with the help of elastic holders, after 30-40 cm, bars-sheathing are installed, on which gypsum boards are attached from below.
- On the upper surface of the resulting lattice structure, a fiberglass film is laid and attached with a stapler to the beams, on which mineral fiber plates are tightly laid out, such as: Izorok, Ursa, Isover, Knauf, Izomin, Rockwool, with a layer of 50 mm, with a transition to the side faces of the beams.
- In rooms of the next level, a layer of chipboard (16 ÷ 25 mm) is nailed onto the beams, after that, a hard mineral fiber sound absorber (25 ÷ 30 mm), and chipboard boards of the "floating" floor are laid again.
Bituminous slate roof
 Soft slate (also known as ondulin slate, ondulin, euro slate, bituminous slate, bituminous slate), in fact, is a molded cardboard-cellulose material, fixed with a distilled bitumen compound and colored with a polymer, UV-resistant, coloring composition. bituminous slate is made under various brands (Bituwell, Aqualine, Nuline, Onduline, Guttanit, Ondura, Corrubit). The usual dimensions of corrugated sheets: 2000x950, the number of waves is 10.
Soft slate (also known as ondulin slate, ondulin, euro slate, bituminous slate, bituminous slate), in fact, is a molded cardboard-cellulose material, fixed with a distilled bitumen compound and colored with a polymer, UV-resistant, coloring composition. bituminous slate is made under various brands (Bituwell, Aqualine, Nuline, Onduline, Guttanit, Ondura, Corrubit). The usual dimensions of corrugated sheets: 2000x950, the number of waves is 10.
The main qualities of bituminous slate roofing are the speed of construction and affordable cost. In terms of weak points, it is worth mentioning a fairly short-lived loss of color vibrancy, as well as a noticeable combustibility of bitumen-cardboard material, compared to metal tiles.
The roofing material is laid on a solid base made of a sheathing layer and rafters.
In the case of private buildings, a two- or three-span structure is usually used with intermediate supporting walls and sloping rafters.
The interval between the rafter legs is usually performed in the range of 0.60 ... 0.90 m with a width / thickness of the rafter legs 5x15 ... 10x15 cm; the supporting ends of the rafter beams are fixed to a fixing beam measuring 100x100 ... 150x150 mm.
- The transverse overlap of the bituminous slate sheets and the frequency of laying the sheathing are determined by the slope of the roof slope: if the angle is more than 15 degrees, then the gap between the boards of the sheathing structure is set to 0.30 ... 0.35 m, and the overlap is 17 centimeters.
- It is better to fasten corrugated sheets of ondulin from the lower zone of the side part of the slope, opposite to the leeward side, to protect them from wrapping during hurricane loads.
- The next layer is laid with a shift of half a canvas, from the canvases of the underlying tier, in order to avoid unnecessary layering in the joints of four adjacent sheets, which contributes to the formation of leaks.
- Sheets of euroslate are fixed along the bottom edge into each wave crest, along two intermediate crate boards into odd wave crests, and the top is covered with an overlap of the upper sheet or a ridge detail. To fix each corrugated sheet, about twenty self-cutting roofing screws (size 65.0x5.5 mm) or nails are enough: length / diameter -73.5 / 3.0 mm with elastomeric washers.
- Ordinary overlapping of canvases is enough to arrange in one wave, and with a roof slope of less than 10-11 degrees. - in 2 corrugated waves.
- The ridge is strengthened from the side of laying corrugated sheets, with an overlap of 0.2 m, with screws screwed into each corrugation vertex of the underlying corrugated fabric.
- In order to protect and decorate the side sections of the roof slope, chip profiles are used, the fixing of which starts from the corner above the eaves, overlapping by 0.2 m.
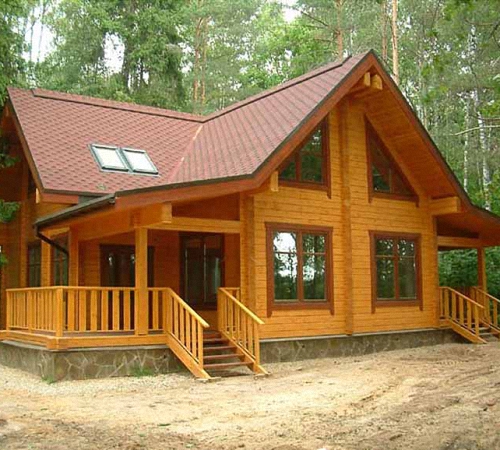
It does not matter whether you have found a decent construction company or decided to make a house out of timber with your own hands - at some stage you just need to calculate the amount of lumber required to build it. What do you need to know for this? Firstly, how much and what kind of timber is needed for the house. Secondly, how much is approximately in one cubic meter. And only then you can carry out a simple calculation of the cost of construction and even draw up an approximate estimate.
We calculate the amount (consumption) of timber per house
Immediately make a reservation that all the calculations below for the amount of timber per house are approximate. More accurate volumes of the required material can be determined based on the specific project of a wooden house. On walls made of timber, the cubature of lumber can be calculated as follows:
- calculate the perimeter of the house;
- multiply the perimeter by the height of the floor;
- we multiply the obtained value by the thickness of the timber used to build the house;
- as a result, we have the number of cubes that is necessary for the construction of one floor
If, in addition to external walls, the presence of internal partitions (also made of timber) is also implied, then they are additionally taken into account. If desired, you can calculate not only how much timber is needed per house in terms of volume, but also in pieces. To do this, it is enough to divide the resulting volume by the volume of the piece product.
Let's give a concrete example: it is necessary to build a small cottage 5×7 m with a simple attic and one partition. Ceiling - 3 m. In this case, a beam with a cross section, for example, 150 × 150 mm, will be used. The pediment will also be laid out of timber. Our calculations will look like this:
- the perimeter of the house, taking into account the length of the partition: (5 + 7)? 2 + 5 \u003d 33 m;
- the volume of the walls of the first floor: 33? 3? 0.15? 15 cubic meters;
- the cubature of the beam that went to the pediment is considered approximately as half of the material required for the construction of two walls 5 m long and 3 m high: 5 × 3 × 0.15 \u003d 2.25 cubic meters.
In total, about 17.25 cubic meters will go to the walls. timber or, taking into account 20% of the stock, about 20 cubic meters. m. material. But it should be understood that here we did not take into account, for example, floor beams made of glued laminated timber (regular or profiled), as well as other design features: window and door openings, for example, on the contrary, will reduce the need for lumber. Therefore, you can safely add 5 cubes. As a result of such approximate calculations, it turns out that the construction of our house will take about 25 cubic meters of timber.
How many timber in a cube
Simple calculations allow not only to calculate the cubic capacity of a beam per house, but also to determine almost the exact number of beams. This is easy to do: it is enough to know the required volume of lumber and the volume of a piece product. It remains only to divide the first by the second - we get how many pieces of beams are needed to build a house. Below we have presented a table in which we examined the most common cross-sectional dimensions with a material length of 6 meters.
Beam dimensions
The size of the timber used in the construction of the house matters, but everything must be approached from the point of view of economic feasibility. It's about, for the most part, about the thickness of the walls and the heat-conducting characteristics of the material. Below we will consider the issue of timber thickness in two cases: during the construction of a summer (country) house and a building for permanent residence.

Thickness and width
The width of the beam should worry the developer only if it is planned to permanently live in a house built from it, and even then not always - after all, any wooden wall can be insulated with effective thermal insulation, thereby avoiding losses for "street heating". So, if you are planning to build a conventional country house, then it is quite possible to use a material with a cross section of 100 × 100 mm. Using ordinary unplaned material, you still have to deal with issues with facade cladding and interior decoration, dealing, for the most part, with the problems of the aesthetics of the house. But when building a house for permanent residence, it is better to use a profiled beam with a width of 150 mm or more. In this case, you still have to insulate the walls. As for the thickness, everything is simpler here - it just depends on the number of beams needed to build walls. But, meanwhile, this also affects the number of seams between the crowns. Summarizing the above:
- thickness and width of timber for country house practically does not matter (with seasonal residence in the warm season);
- for permanent residence, you can choose a material of greater width, but you still have to insulate the walls. And you can save on the cubic capacity of the timber, while relying on high-quality insulation - it will turn out cheaper and more efficiently in terms of reducing heat losses
So, in order to build a really warm house only from a bar, the thickness of its walls for the Moscow region should be about half a meter. The same effect will be when using a beam 150 × 150 and 10-15 cm of thermal insulation.

Please note that not all manufacturers and sellers of lumber are honest with their customers: you can often encounter a situation where the dimensions of the beam section are less than those indicated. For example, a bar 150x200 actually turns out to be a material with dimensions of 140x190 or even less. Be sure to check the actual parameters of the timber before buying! This will help you not to get into a mess, save money and nerves!
Estimate for a house from a bar
Before you decide on the choice of a construction company that will build your house, you should start monitoring offers. How to determine the most cost-effective option? Everything is very simple - request an estimate for a house from a bar according to the selected standard or individual project. In such an estimate, ALL costs associated with the construction of the house must be indicated. This includes the cost of all building materials, and in fact, the payment for the implementation of all types of construction work.

Having chosen several construction companies that you liked, you should request an estimate for a house made of timber. Normal companies offer them for free. It is noteworthy that for different companies, estimates for the same buildings can differ not only by 10-20%, but also at times - it all depends on the appetites of the builders. It is advisable to have on hand the most detailed list of works and materials required for building a house according to your project. This is the only way you can avoid unforeseen expenses that usually pop up already at the stage of building a house.
If desired, an estimate for the house can be compiled independently: for this, it is necessary to calculate the consumption of all materials and multiply their quantity by the average price. To this, you will have to add an amount of approximately 50-100% of the cost of building materials - the price of work. You will get a very approximate calculation of the cost of a house made of timber, but it can be used to analyze offers from specialized companies.

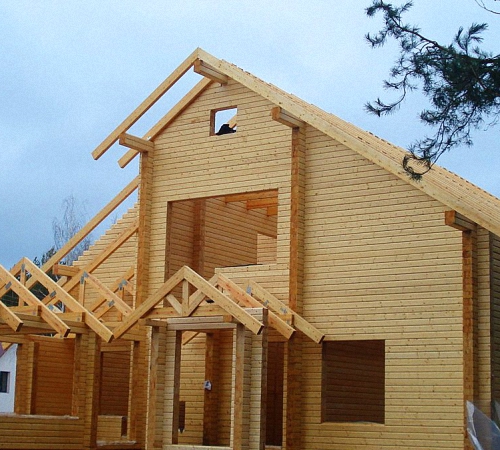
Building a house from a bar opens up a lot of advantages for its owner, the main of which is the environmental friendliness of the chosen material. The process of calculating and choosing the material precedes the construction of the house, and we will talk about it further.
Timber house - varieties and advantages
Making houses from timber is becoming more and more popular. Since this material is harmless, and even beneficial to health. Living in a house made of wood has a beneficial effect on well-being. Since, wood is able to regulate the optimal level of humidity in the room.

For the manufacture of timber, solid wood is used, from which rectangular beams are cut. The most commonly used material is coniferous trees. Since they are distinguished by the highest level of resin content, which makes the material more durable and prevents it from rotting, thereby increasing the service life.
There are two types of timber:
- ordinary type;
- profiled.
The standard type of timber is a timber with a square or rectangular section. The procedure for manufacturing profiled timber is more complicated, as it requires cutting out locks, grooves and ridges. This beam is more convenient in connection and the room that is made from it has the highest thermal insulation characteristics.
In relation to the structure and production technology of timber, the following material is distinguished:
- whole;
- glued type.
For the production of the first version of the beam, the presence of solid trees is required, from which the beam is cut. To make a glued-type beam, it is necessary to have boards of a certain size, which are glued and pressed together. For additional resistance to decay, antiseptics are applied to the boards, and then interconnected with resin. This type of timber is more resistant to cracking, but not fireproof enough. It is possible to manufacture glued laminated timber using various kinds of wood, for example, spruce and pine. In the process of gluing, the main thing is not to allow the fibrous parts of the boards to coincide with each other, since the beam, in this case, becomes less durable.

In addition, in the process of manufacturing glued beams, boards on which defects are present are not used, but replaced with new ones.
The most important and indisputable quality of any type of timber is its environmental friendliness. Since solid wood is used for its manufacture, which has all useful properties natural wood. If we compare glued and solid timber, then the second option is more environmentally friendly, since the resins used for gluing glued timber emit toxic substances in small quantities.
Although in architectural terms, the use of glued laminated timber is more convenient. Since with its help it is possible to build buildings of any shape. The standard length of glued laminated timber is 6 m, but there are cases when logs reach a length of 15 m.
A house made of profiled timber allows you to hide communications by cutting out special niches. The building, in the manufacturing process of which glued laminated timber is used, is more fire resistant, since in the process of its manufacture each of the boards is impregnated with fire-resistant mixtures, which make it incombustible.
Among the disadvantages of making a house from a bar are:
- if the material is not properly dried, it is not able to perform all its functions with high quality;
- requires constant application of impregnations that improve its quality characteristics, otherwise, the tree begins to rot and deteriorate;
- glued laminated timber has a very high cost, which is its big drawback, although it is fully justified by the complexity of its manufacture and durability in operation.

How to calculate a beam: features of the implementation
When buying a bar, its cost is measured in cumobetry. Therefore, this unit is also used for glued calculation beams or edged boards. To determine the amount required material, you should first find out its size. For example, with a width of 15 cm, a length of 6 m, and a thickness of 10 cm, the number of logs is determined by dividing one cubic meter by the volume of the timber. One cubic meter of this timber contains 11 logs.
The calculation of the amount of timber per house involves the determination of materials for its various sections.
The first to be calculated are the ceiling and floor beams. When building a house on unstable ground, it is advisable to replace the floor on beams with a monolithic base. Otherwise, the use of wood is recommended. The standard size of the ceiling beams and floor type is 10x15 cm. The step of their laying is not more than one meter. For maximum strength, beams should be cut into each other in a vertical position. To calculate the total length and number of required beams, you must perform a series of actions:
- divide the total length of the house by the step of laying the beams, and then subtract 1.
For example, if a house has a length of 6 m and a width of 5 m, with a laying step of 1 m, the beams are calculated as follows: 5/1-1=4 pieces.
The beams are produced in a standard length of 600 cm, which is the same as the length of the house.

The next stage is the calculation of the cubature of the timber, for the construction truss system. We offer an example of a calculation option for a straight gable roof. In this case, the installation step of the rafter is 600 mm, and the angle of inclination is 45 degrees. For the manufacture of rafters, a material with a cross section of 10-15 cm is used. Please note that with an increase in the angle of inclination, the amount of snow that accumulates on the roof in the winter decreases, and the load on the building decreases, although the resistance of the roof to the wind also becomes less. Therefore, for regions with increased windiness, it is recommended to build a roof with a low angle of inclination, and in places with a lot of precipitation, in the form of snow, it is better to give preference to a roof with high level tilt.
In order to equip the rafter system, you must first install two rafter legs, and then fix them with a beam. Next, the rafters are installed.
If the value of the run of the house is 1000 cm, and the angle of inclination is 45 degrees, then in order to calculate the length of the rafter leg, it is necessary to calculate the sum of the legs squared. This value will be 424 cm. For the construction of each triangle, you will need to purchase 850 cm of material.
To calculate the number of triangles, we divide the total length of the roof, which is 1000 cm, by the laying step - 60 cm, and subtract one, we get 16 pieces. Now we multiply the number of triangles by their length - 16 * 850 = 13600 cm. In addition, one should not forget about the run, which is 1000 cm, we add it to the main value and get 145 m of wood. If the cross section of the beam is 5x15 cm, then to calculate the number of cubic meters, you need 145 * 0.15m * 0.5 \u003d 10.9 cubic meters.

The calculation of the beam load on the surface of walls, gables and internal partitions is carried out in relation to the building project. When carrying out the calculation, one should proceed from one approach to calculating the material for internal partitions and walls. All elements should be converted into geometric shapes and, based on the formulas for each, determine their area. If there are openings in the form of windows and walls, their area should be determined. Subtract the opening area from the pre-calculated wall area, multiply the resulting value by the wall thickness and you will get the amount of material that will be needed to build the wall. After calculating the value for each of the walls, summarize the results.
The calculation of the strength of the timber depends on its weight, which is affected by the rock and humidity. The latter value is determined by the percentage of the amount of water in the tree. The humidity value determines the quality of drying and storage conditions of the material.
Dry wood is a material that has been dried under technological conditions, or stored in warm and dry rooms for a long period of time.
Raw wood is called a tree that begins to dry. If the material contains equilibrium moisture, then it is classified as air-dry wood. When the material is stored in conditions of high humidity, it takes the form of a wet or freshly chopped tree.

The construction of a house with the use of timber is easier to carry out calculations, compared with houses made of logs. In addition, the use of timber opens up before the owner of the house a large number of options for finishing both the interior and exterior of the building.
In relation to the cross section of the beam, materials are distinguished: 12x12, 15x10, 18x18, 20x15, 15x15, 10x10, 14x14. The most optimal size of timber for building a house is 15x15 cm. Since it is this type of timber that has an acceptable cost and high thermal insulation characteristics. In addition, this beam is easy to install and easy to operate.
The use of profiled timber with such a section will allow you to build an excellent house that will serve its owner for many years. The only drawback of this beam is its high cost, therefore, when calculating a profiled beam, you should be extremely careful not to make a mistake and not spend a lot of money.
To correctly calculate the amount of material with which you want to build a house, use the formula:
A * B * C \u003d number of timber
A is the length of the wall;
B is the height of the wall;
C is the thickness of the material.
For example, for the construction of a house, the length of which is 8 m, and the width is 6, using a beam with a section of 15x15, calculations are carried out according to the formula: 2 (6 + 8) \u003d 28 m - the value of the perimeter. The height of the wall is three meters, so this value is multiplied by the perimeter, we get 54 m. Now we multiply the result by the cross section of the beam, which is 0.15 m, we get 8.1 cubic meters. Therefore, this will be the value of the amount of timber needed to build a house.

How much timber is needed to build a house
Factors on which the amount of timber for the house depends:
- type of timber used in the construction process;
- the amount of timber in one cubic meter;
- house design.
To calculate the amount of timber for external and inner wall, use the algorithm:
1. Calculation of the perimeter of the building.
2. Multiplying this value by the total height.
3. Multiplying the result obtained by the cross section of the beam.
4. It turns out the amount of cubic meters of material needed to build the building.
In the process of making calculations, attention should be paid to the fact that the device of the first crown will require more material, since its width must be increased. In this calculation algorithm, this condition is not taken into account, therefore, to calculate the bar of the first crown, a separate formula must be applied.
The cross section of the beam for the first crown should be chosen more than the main one, since it is this crown that is bearing and takes on the entire load from the building. In addition, it requires additional processing with engine oil or an antiseptic solution.
When the calculation of the beam for bending is completed, the procedure for determining the number of pieces of timber for building a house follows. This value will help save time during the material purchase process. In addition, in this way it will be possible to avoid fraudulent actions on the part of the seller.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the main values \u200b\u200bof the quantities of timber in one cubic meter, taking into account the length of the material of 6 m:
- 10x10 cm approximately consists of 16.6 pieces;
- 10x15 cm - 11 pieces;
- 15x15 - 7 pieces;
- 10x20 - 8 pieces;
- 15x20 - 5.5 pieces;
- 20x20 - 4 pieces.

To determine the amount of timber in pieces, the total value, for example, 14 cubic meters, should be divided by the volume of one piece of timber in a cube. To calculate this number, you need to divide the cross section of the beam by the number of pieces in one cube. For standard size timber 15x15 cm, this is 0.13. 14/0.13=107.6 pieces.
When setting the number of pieces needed to build a building, there is no need to accurately measure each cubic meter when buying material. Enough piece-by-piece counting of the material.
The height and width of the beam play an important role in the construction and operation of the building. In a higher beam, the interventional seams are reduced and the construction procedure is accelerated. When choosing the optimal width, the need for permanent or temporary residence in the house is taken into account. Minimum Thickness timber, recommended for the construction of a building in which people will permanently live, is 20 cm. At the same time, to improve thermal insulation, foam or mineral wool is used, laid in a layer of 10 cm. If it is planned to build a bath, then the layer thickness should be increased to 16 cm.
In the process of building a country house, in which people will live only in the summer, it is enough to purchase a beam with a section of 10x10 cm.
When calculating a stepped beam, an important factor is the preliminary design of the building. It is on the project that both the external and internal views of the house, the number of walls, doors and windows are displayed.
There are several options for obtaining a project:
- its own production;
- order from specialists;
- purchase on the Internet;
- project purchase;
- use of the finished project.

To independently create a project at home, you need special skills in working with drawings. For its compilation, the climate in which the house is located, the soil on which it is based, and other factors are important.
Therefore, the most right decision will hire specialists who are able to take into account all the individual characteristics of the site.
Remember that when calculating a timber for building a house, it is better to buy material with a small margin than to stop construction work due to its lack.
A house built of timber has many advantages. The material is characterized by the correct shape, so the useful space is obtained in the room. If you decide to build a house out of wood, one of the important points is the calculation of the timber for the house. And it doesn’t matter whether you decide to build a building with your own hands or with the help of professionals.
Example 1. A project with the dimensions of a house for calculating a bar.
To make the correct calculation, you need to decide how much and what timber is needed, as well as find out how much material is in 1 m³.
So, you will quickly orient yourself on the price and upcoming expenses.
How to calculate the amount of timber per house
For ease of calculation, prepare:
- paper;
- pencil;
- calculator;
- roulette.
Please note that the given calculations of timber per house are approximate. And a more accurate picture can be drawn up, already having the final project of the future home.
- measure the perimeter of the building;
- multiply the perimeter by the floor height of the house;
- multiply the resulting figure by the thickness of the material that you will use in construction;
- in the end you will get the number of cubes that will be needed to build one floor.
If, in addition to external walls, internal partitions are also provided, this must also be taken into account. If necessary, you can calculate the timber for the house not only in cubic meters, but also in units. To do this, you need to divide the volume by the volume of the unit of the product.
Example 2. The project of a small house made of timber.
For clarity, consider the following example. Let's say you have to build a 1-storey house 5 * 7 in size, with one partition and an attic. The ceiling height is 3 m, the pediment is also made of timber. A tree with a section of 150 × 150 mm will be used in the work. The calculations will be as follows:
- the perimeter, taking into account the partition, is 33 m: (5+7=12)*2+5;
- the volume of the walls of the 1st floor is 33 × 3 × 0.15≈15 m³;
- the volume for the gable should be calculated as 1/2 of the material required for 2 walls 5 m long, 3 m high; - 5 × 3 × 0.15 = 2.25 m³.
Thus, after performing simple calculations, we get that 17.25 m³ is needed for the walls. It does not take into account window and door openings, floor beams. The material must be purchased with a margin. Therefore, 25 m³ will be required.
Back to index
Material size
Important parameters are thickness and heat-conducting properties. For construction summer cottage and houses of permanent residence, material of different thicknesses is needed. In the first case, the thickness and width are not of fundamental importance; a material with a cross section of 100 × 100 mm is suitable. In the second case, a beam of greater width is needed, with a section of 150 mm or more. In this case, it will be necessary to perform thermal insulation of the walls. The number of elements required for the construction of walls depends on such a parameter as thickness. But this will also affect the number of interventional seams. If you want to save on material, you need high-quality thermal insulation.
For example, to build a warm house only from a bar, the wall thickness for central Russia needs about 50 cm. You will get the same result when using a section of 150 × 150 mm and 10-15 cm of insulation.
When buying, be careful, sometimes sellers deceive buyers, giving out cross-sectional dimensions as larger than they really are. So, instead of the indicated dimensions of 150 × 200, it turns out to be 140 × 190. Therefore, before purchasing a tree, double-check its actual size. Thus, it is not difficult to perform calculations. This will help you avoid unnecessary expenses. And if you build a house correctly, it will serve you for decades.
Estimating the beam as construction material for the construction of low-rise suburban buildings, we have repeatedly voiced one of its advantages: it is very easy to use, which makes it possible independent production wooden log cabins. This is especially true for such small structures as baths. If you have no practice in carrying out construction work, then building a bath from a bar with your own hands will be a good experience, which can later be used to implement larger plans, for example, building a private house. Indeed, in general, the technology of building a house from a bar and a bath is in many ways similar.
A small guide to self-assembly of a bath from a bar
The abundance of bath projects and their features make it impossible to create a complete instruction for the construction of some kind of universal object. Therefore, within the framework of this article, we will outline only the main points that need to be taken into account in the course of preparatory and construction work.
Type and thickness of timber for a bath
“What kind of timber to build a bath from?” - this question is asked by every developer who has ventured to self-assemble a log house. Each type of material has its advantages and disadvantages, it remains only to determine which of the above is of paramount importance. Looking ahead, we will make a reservation that today baths are most often built from profiled timber, moreover, lumber of natural moisture.
| Type of timber | Nuances of use |
|---|---|
| Edged | The cheapest lumber. The surface is untreated, so most often the walls are sheathed on both sides with a suitable finishing material: timber imitation, clapboard, blockhouse, etc. |
| planed | The surface is smooth, processed, and therefore such a beam is more expensive than edged. A noticeable interventional insulation spoils the appearance of the log house and is the reason for the finishing |
| Profiled (array) | Optimum, in our opinion, lumber in terms of "price-quality" ratio. May vary in humidity. The log house does not require serious finishing, interventional seams are windproof |
| Profiled (glued) | Expensive, but reliable solution. Minimum shrinkage, minimum finishing costs, fast commissioning |
As for the thickness of the beam for the bath, then it is difficult to give an unambiguous answer. If you plan to bathe only in the warm season, then it is quite enough to use a beam with a thickness of 100-150 mm. For a winter bath, you can also use the same lumber - it all depends on your requirements for this building. Another parameter is the height of the crown. The larger it is, the fewer these crowns and the seams between them, thereby the building becomes more monolithic. It is important that this reduces the complexity of the construction of the log house, because. it depends on the number of crowns (fastening with dowels, sealing the seams, etc.).

Calculation of a bar for a bath
We will assume that you have decided on the project and represent the dimensions of the future bath. Let's try to estimate the amount of material required for the construction of the walls of the log cabin of the bath. This is the same as calculating the amount of timber per house. Knowing the parameters of the accepted beam and the layout of the building, we calculate the beam for the bath. For example, a bathhouse has 4 walls of 4 m each. A beam is used with a section of 200x200 mm and a length of 4 m. The number of crowns in a log house is 13 pcs. We have: (4+4)*2*13=208 m.p. timber. From here, the number of cubes per log cabin will be: 208 m.p. * 0.2 * 0.2 \u003d 8.32 cubic meters. m. This is a rough estimate that does not take into account the presence of window and door openings.
wall material prices
We do not provide here tables with prices for specific types and sizes of beams for a bath. We advise you to simply follow the links with the section sizes you are interested in:
- timber 100x100 mm;
- timber 100x150 mm;
- timber 150x150 mm
If you intend to use a bar with other parameters, then look for additional information in the section "Beam Houses" on our website. All articles are recommended average market prices.
How to assemble a bath from a bar?
Direct construction wooden bath starts with the base device. We advise you to choose the foundation that best suits your conditions. For more information, look in the section "Foundation for the house" on our website. After pouring the foundation, its horizontal part is covered with two layers of waterproofing, for example, roofing material. This will minimize the risks of wetting the first crown of the bath from the timber. As the first element of the log house, it is better to lay a larch laying board with a thickness of 50 mm or more. It will be easier to replace it, if necessary, than a bar. The lower part of the log house is the most vulnerable (subjected to moisture and rots), therefore it is better if the first crowns are larch timber, connected at the corners into half a tree. To seal the joints between the bars, a layer of jute material is laid, each two crowns are connected with dowels, thereby forming a rigid structure. The floor logs of the first floor are cut into the lower trim or into the second crown with a dovetail connection. Partitions are made immediately after the construction of the log house, as a rule, along the log lines. After the erection of the walls, they proceed to the device of the truss system. The simplest option is gable roof with an uninsulated attic (only the ceiling is insulated). Gables for savings are made according to frame technology, sheathing them subsequently with an imitation of a bar.

About insulation and finishing
Usually in baths only the floor and ceiling are insulated. For these purposes, mineral wool slabs 50 mm thick, laid in a checkerboard pattern (overlapping the joints), are perfect. The insulation must be protected on both sides with waterproofing. Interior decoration baths from a bar, subject to the use of profiled material, implies a finishing floor (grooved board), lining the ceiling with clapboard, vapor barrier and lining with aspen or linden eurolining of the walls and ceiling of the steam room.
Finally
This is what building a bath from a bar with your own hands looks like. You can find more information in the videos provided.