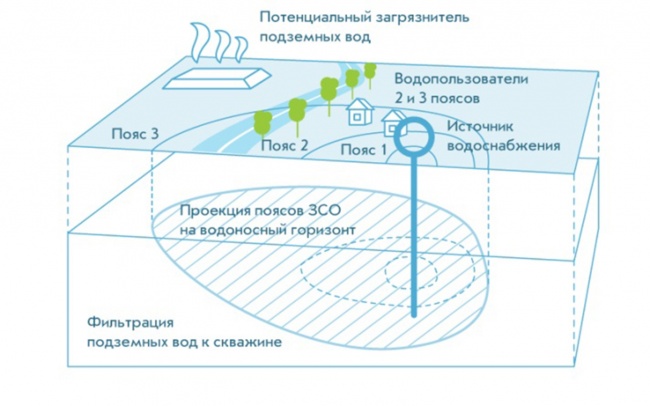
To obtain water from an artesian well, special equipment is used. Sanitary zone, located around it, is designed to protect the formation containing water from contamination. There are several security belts that should be considered in more detail. In a restricted area, special actions are carried out that prevent pollution of the aquifer. After exploration and design, a water well passport is drawn up.
Main Factors
When creating a special protection zone, the type of pollution should be taken into account. Their chemical stability needs to be determined. In addition, it is important to know the amount of movement of contaminants in the aquifer. The path that the pathogenic microflora has taken is determined by the number of microbes and their strains. The following factors should also be taken into account:
- period of viability of pathogenic microorganisms;
- geological conditions;
- the time that the pathogen is able to retain harmful properties.
The last factor is one of the most significant. When designing a protective area around an artesian well, absorption capacity and some other factors should be taken into account.
Important! A warning sign must be installed on the first belt.
When planning a sanitary zone, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of chemical contaminants that are consistently found in the aquifer. It is necessary to determine their concentration and composition. This need is explained by the direct contact of pollution with downstream groundwater.
When creating a sanitary protection area, it is necessary to monitor changes in the chemical indicators of pollution. This should be especially monitored when designing water wells.

Hydrogeological conditions
The development of the exact dimensions of the WSS and its equipment implies planning for the protection of the territory where the well will be located. It is necessary to take into account a number of factors affecting the size of the zone.
- type of water intake;
- performance;
- the depth at which groundwater is found.
When using protected waters, attention should be paid to the presence of a waterproof roof in all belts. If the rock is unable to protect underground lakes, it is necessary to take a number of measures aimed at eliminating the means of pollution.

The protective zone is created taking into account the data of many studies. They include the study of the microbiological environment, the characteristics of the aquifer. The construction of an artesian well and the implementation of a project for a protected area require coordination with the plan for domestic water supply.
Established zones
For an artesian well, it is necessary to form a protective zone of the first belt. A distinctive feature of the first belt is the absence of various impurities that can come from the surface.

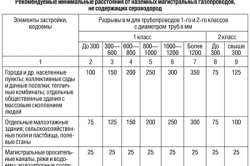
For an artesian well, the protection area should be located more than 30 m from it. When a well is located in an unprotected horizon, there is a high risk of various contaminants entering the water.
If there are no pollution sources on the territory, the ZSO is reduced to 15 m. The first zone must meet certain requirements. This is especially true for the location of various economic facilities.

Sanitary protection zone
When determining the boundaries that can protect the well from bacterial contamination, many factors should be taken into account. If you miss them, the quality drinking water will decrease noticeably. In order for the well to produce potable water, the basic requirement must be met - water should not penetrate to the well from outside the boundaries of the protective territory.
Before planning a sanitary zone, a certain parameter should be calculated - the time during which polluted waters move from the farthest point of the protection area to the water intake system. Such an indicator is designated "Tm". If poorly protected waters are found as a result of hydrogeological studies, this characteristic is 400 days. With protected waters, Tm is equal to two hundred days.

Borders of the third sanitary belt
The boundaries of the third belt are determined on the basis of the estimated time of movement of pollution, equal to 25-50 years. The boundary is found by hydrodynamic measurements. The specified time (25 years) represents the entire period of operation of the water intake. This design characteristic is called Tx. From the border of the third belt to the water intake system, pollution should not move earlier than the estimated time Tx.
There should be no reverse flow when measuring the boundary of the third zone. The minimum is 250. When determining this boundary, it is necessary to take into account the terrain in which the well is installed. When installing a water intake on a plain, this boundary will be made at a distance of 500 m, if it is located in the mountains, the range should be 750-1000 m.

The boundaries of the third protection zone may vary depending on the territory of the second water protection zone. In such a situation, a special permit is obtained from the sanitary and epidemiological supervision. The project for drilling a well for water must meet all the requirements.
Necessary actions
To protect the water intake area from various contaminants, you will need to perform certain actions. To do this, the first zone must be fenced and landscaped. It is forbidden to plant trees on the territory. Various fertilizers and chemicals are also banned. In order to prevent water pollution, guards should be set up at the site with water intake.

The flow and flow of water are controlled by special equipment. Various plumbing structures are located in the first protection belt. They are equipped with special devices, thanks to which water cannot be contaminated through pipes.
ZSO, which has a second belt, must be properly prepared. It should be cleared of unproductive wells. Such structures can quickly pollute the aquifer. Drilling equipment is not installed in the area that belongs to the second protection belt. In this area, the injection of waste water is prohibited.
Do not use well water for bathing purposes on the second
ZSO. In addition, no chemical fertilizers can be sprayed here.

The area where the artesian well is located is limited to green spaces or a fence. Usually the size of the first sanitary zone is 0.25 ha. Wells are installed in accordance with all requirements. This ensures maximum purity of the produced water.
Before calculating the boundaries of protective belts, painstaking work is carried out. In the process of reconnaissance, advanced equipment is used. Only after taking into account all the advantages and disadvantages different options make a decision to install a well.

The first sanitary zone of a drinking water well should be located on a site of 30x30 or 60x60 m. The perimeter is limited by a fence or hedge. The well should be made in the center of the allocated area. If 2 wells are installed, the site must be expanded without changing the length.
In the case of an unprotected horizon, the size of the territory can be increased. If the well is located on the edge of a protected area, this is a gross violation. The documentation for the well cannot be issued if the radius of the first sanitary zone is 9 m. If this figure is 5 m, the design of the protection zone will not be approved by the relevant authority.
The project of "Well Sanitary Protection Zones" is being developed in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02 and includes:
- determination of the boundaries of the zone and its constituent belts;
- an action plan to improve the sanitary condition of the territory of the WSS and prevent pollution of the source;
- rules and regime of economic use of the territories of the three belts of the WZO.
About sanitary protection zones
Sanitary protection zones are organized as part of three belts: the first belt (strict regime) includes the territory of the location of water intakes, sites of all water supply facilities and a water supply channel. Its purpose is to protect the water intake site and water intake facilities from accidental or intentional pollution and damage. The second and third zones (zones of restrictions) include the territory intended to prevent water pollution of water supply sources.
The developed project is undergoing examination at the FGUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology" with an expert opinion. Then, on the basis of it, the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare (Rospotrebnadzor) issues a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on the zones (reduction of zones) of the sanitary protection of the well.
In addition to the calculation of the WSS, the project includes a hydrogeological and sanitary and epidemiological description of the site where the wells or water intake are located. Work completion time: from 2 to 14 months, depending on the set of initial documentation (Project development, laboratory tests, approval).
Underground water sources
- Hydrogeological conclusion on the possibility of using groundwater (issued by RosGeoFund (SevZapNedra) based on the results of a well survey);
- At least 3 water samples per season for organoleptic, biological, sanitary, radiation and indicators chemical composition water quality;
- Hydrogeological data (characteristic of the area where the artesian well is located);
- Sanitary and epidemiological report on radiology;
- Technical passport of the art well, geological section of the art well;
- Registration card of an artesian well;
- Contract for water disposal;
- Passports (certificates) for pumps and filters (if any);
- Water analyzes in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 "Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality in centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control"
- Action plan for the 2nd and 3rd belts, agreed with all land users falling within the radii of these belts.
- Situational plan of the first zone of the ZSO on a scale of 1:500, 1:1000; Situation plan of the second and third belts of the ZSO on a scale of 1:10000 - 1:25000 with the drawing of all objects located on this territory. Both plans must be signed by the district architect.

Surface sources of water supply
- Water use license and license requirements;
- Minutes of the meeting (Extract) of the State Commission for State Expertise of Mineral Resources (SevZapNedra);
- The prospect of water withdrawal (within 5-10 years, water withdrawal is planned to be increased, reduced or left at today's level);
- hydrological data;
- Analysis of water consumption (who consumes and in what quantities);
- Water analyzes in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 "Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality in centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control".
Water analysis protocols:
- Monthly studies for the last 12 months on microbiological and organoleptic indicators of water;
- The last 4 analyzes (according to the seasons of the year) for organic and inorganic substances;
- Annual analysis of water for radiation indicators (for Last year). Expert opinion on compliance or non-compliance of radiation indicators with standards.
- Action plan for the 2nd and 3rd belts, agreed with land users falling into these belts.
- Situational plan for drawing the first belt of the sanitary protection zone on a scale of 1:500 or 1:1000;
- Situational plan for drawing 2 and 3 belts of sanitary protection zones with drawing places of water intakes and sites of waterworks, a source of water supply and its supply basin (with tributaries) on a scale of 1:50,000 - 1:100,00
- With the drawing of all objects located in the given territory (enterprises, farms, buildings, cemeteries, agricultural fields, cattle burial grounds, waste landfills, etc.).
- Both plans must be signed by the district architect.
- Water use license with applications.
In addition to the calculation of the WSS, the project includes a hydrogeological and sanitary and epidemiological description of the site where the wells or water intake are located. The project of sanitary protection zones is coordinated with Rospotrebnadzor. Measures for the 2nd and 3rd belts must be agreed with the owners of the land falling within the radii of these belts.
About sanitary protection zones
At the source of water supply, in particular the well, there are several zones of sanitary protection.
ZSO of the 1st belt, which is also called the strict regime zone. It is installed with a diameter of 60 meters (with a radius of 30-50 m from the well to the fence) according to SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02, but only if there is an overlapping thickness of the regional aquiclude - clays overlapping limestone (in St. Petersburg and Leningrad region the first centralized aquifer is protected by the Baltic shield, i.e. overlain by an area of Precambrian folding). Zones of sanitary protection of water supply sources and drinking water pipelines. The ZSO of the water supply source coincides with the perimeter of the site fence (this zone is also called the ZSO of the 1st belt), this zone is agreed with the TOU Rosprirodnadzor (local authority).
If it is required to reduce the ZSO of the 1st belt, then it is necessary to write a draft justification for reducing the sanitary protection zone of the water supply source.
The following documents will be required for the development of a project for the SPZ of an art well:
- General plan of scale 1:500 (1:1000 or 1:2000 for large enterprises);
- Situational plan of scale 1:2000 (or 1:5000, 1:10,000);
- Well passport with geophysical surveys;
- Calculation of water consumption and water disposal;
- A valid license for subsoil use (extraction of fresh water);
ZSO of the 2nd belt for bacteriological contamination. ZSO of the 2nd belt is determined by calculation, based on the flow rate of wells, the thickness of limestones. The flow rate of the well is determined by the calculation of water consumption and water disposal.
The project of sanitary protection zones is the rationale for the placement of local treatment facilities (VOCs) at the construction site. VOCs should be located outside the 2nd zone of the sanitary protection zone of the water supply source (in this case, a well);
ZSO 3rd belt for chemical pollution. ZSO on chem. (chemical) pollution is the ZSO of the 3rd belt and is also determined by calculation, based on the flow rate of wells and the thickness of water-bearing limestones.
Sanitary zones of artesian wells
Well sanitary protection zones (ZSO) are a platform of a certain diameter around a water intake facility. Its main purpose is to protect the well from accidental contamination. In accordance with SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02, the ZSO is divided into 3 zones of varying degrees of severity and restrictions.
Sanitary protection zone 1 belt
This belt is called the strict regime belt and protects the well from contamination. In this area, the well and all the necessary communications for its operation should be located directly. Buildings, houses, buildings, trees, pipelines, sewers and other things that are not related to your well cannot be placed in ZSO-1. The use of any fertilizers and chemicals is prohibited.
This site must be prepared: a layout for the removal of Wastewater, landscaping work has been carried out, a fence has been installed around the perimeter, the approaches to the well have a hard surface. It is also necessary to equip the wellhead to prevent pollution and use equipment to control the flow rate of the well.
The water protection zone of the well 1 of the belt has boundaries within a radius of 30 m from the well, if the limestones are reliably covered from above with a layer of waterproof clay. In case of insufficient overlap, the sanitary zone 1 of the belt increases within a radius of up to 50 m.
If you have the right sewerage system with the disposal of wastewater to the treatment plant, the absence of any pollutants, properly conducted drilling and well construction, you can reduce the sanitary zone by 2 times.
Having prepared a draft justification for reducing the sanitary protection zone of the 1st belt, it is possible to reduce the radius of the ZSO 1 to 15 m for a protected aquifer and up to 25 m for an insufficiently protected one.
There are a number of organizations involved in the development of these projects.
Sanitary protection zone 2 belts
In the water protection zone of the well of the second belt (restricted zone), cattle grazing, discharge of urban sewage, as well as industrial waste should not be carried out, there should be no cemeteries, burial grounds, fuel depots, poultry farms and other things that negatively affect the soil. In the presence of places of tourism and fishing, hygiene rules must be observed. It is forbidden to use chemicals and fertilizers.
The boundaries of the WSS 2 belt are taken depending on the survival time of microorganisms, with the expectation that a microbe that has entered the aquifer outside the WSS 2 will not have time to reach the well.
Sanitary protection zone 3 belts
The security zone of the third belt protects against chemical pollution. This area should not contain warehouses of fuels and lubricants, fertilizers, chemicals and other things that can cause chemical contamination of the soil.
The area covered by SZZ 3 is calculated depending on the speed of movement of chemical particles, with the expectation that a particle that has fallen outside SZZ 3 will not have time to reach the well during the entire period of its operation. Recall that the time of use of the well is 25-50 years.
- Main Factors
- Accounting for hydrogeological conditions
- Zone establishment
- Sanitary protection zone
- Borders of the III zone of the ZSO
- Necessary actions
Water suitable for drinking is obtained using water intake equipment. The sanitary protection zone of an artesian well is designed to carry out special actions that prevent pollution of the source of water intakes or a water-containing formation located in the area of work being carried out.
Main Factors
In the course of work on the creation of a special protection zone, the contractor must take into account the type of possible contamination, as well as determine their microbial or chemical resistance and the amount of advancement in the water-bearing formation. The segment of the path traveled by pathogenic microflora in an artesian well is determined depending on the types of microbial strains and their total number. At the same time, factors such as:
- geological conditions;
- the time of preservation of the causative agent of its harmful qualities;
- viability period of the pathogenic flora.
One of the main factors influencing the determination of the parameters of the WSS is the period during which microbes are able to retain their pathogenic properties.
The protective zone and its design do not require the determination of adsorption capacity and other factors that can prevent the large-scale spread of microbes.

A warning sign must be present on the first belt of the zone of the security zone.
When designing a sanitary protection zone, the properties of chemical contaminants are taken into account, which have a stable composition and concentration in the water-bearing layer. This process is due to their close contact with the underlying groundwater.
As a result of the emerging connection between individual chemical ingredients and groundwater, the magnitude of the rate of spread of pollution decreases. When creating a sanitary protection zone, attention should be paid to changes in physical and chemical properties pollution, if they are strongly manifested in the course of work.
Back to index
Accounting for hydrogeological conditions
The development of a sanitary zone and the establishment of its exact dimensions provide for the simultaneous planning of measures for the sanitary protection of the territory. A number of important factors affecting the size of the zone are taken into account:
- type of water intake;
- the value of water intake productivity;
- depth of groundwater.
When using protected waters, pay attention to the fact that they have a waterproof roof in all belts. If the rocks are not able to protect groundwater, when planning a sanitary protection zone, a number of measures should be outlined to eliminate the means of water pollution.
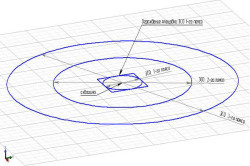
They are transferred from the boundary of the zone to a distance that provides the time for the advancement of microbial or chemical contaminants by a value corresponding to a given one.
Numerous studies underlie the creation of a protective zone: microbiological surveys are carried out, and the main parameters of the aquifer are also studied. The creation of an artesian well and the subsequent design of a protective zone are consistent with the design of domestic water supply.
Back to index
Zone establishment
For an artesian well, a sanitary protection zone, or zone I of the belt, is formed. Its creation is based on the principle of preservation of the aquifer. The peculiarity of the I belt is that the water is not polluted by foreign impurities coming from the surface due to filling from water sources located above.
For an artesian well, the SSS is located at a distance of at least 30 m from its location. If the well is located under an unprotected horizon, groundwater may be contaminated and it becomes necessary to increase the radius: in this case it will be about 30 m.
Special conditions, namely the absence of probable water pollution channels, make it possible to reduce the sanitary protection zone in the first belt to 15-25 m. The first zone has special requirements regarding the location of household and industrial facilities that do not belong to the system that provides water supply.
Back to index
Sanitary protection zone
Numerous bacterial contamination can degrade the quality of drinking water. When calculating the boundaries of the protective zone, it is necessary to determine the boundaries that prevent the penetration of radioactive and chemical substances into the well. The boundaries for the zone are set based on the following principles:
- Water on the territory of the well should not fall from places located further from the border of the well.
- The time of delivery of water from the boundaries of the sanitary zone to the well should be within, but not less than, the period of its operation.
The width of the zone, which is located near the well, in the opposite direction of water movement, is determined by the formula A \u003d 2R 1, where R 1 is the radius. The width of the zone, but already in the direction of water flow, is calculated by the formula B \u003d 2R 2, where R 2 \u003d R 1 /2.
The main parameter, which indicates the length of the section from the zone boundary to the well, is the time for the movement of contaminated water to the water intake equipment. It can be referred to as Tm. If poorly protected waters are found during hydrogeological exploration, then Tm will be 400 days. For protected interstratal waters, the calculation will be a different figure: Tm - 200 days for I and II climatic regions.
Back to index
Borders of the III zone of the ZSO
To determine the boundary in the III belt, the calculation is made on the basis of hydrodynamic measurements. Take into account the fact that polluted waters move towards the intake source for a period of time exceeding the calculated Tx. Tx is understood as the entire period of operation of the industrial water intake, which is 25-50 years.

In the sanitary protection zone of an artesian well, it is prohibited to produce different kinds works that cause damage to water communications.
The calculation of the boundary of the third belt is established in the complete absence of reverse flow and is at least 250 m from the location of the well.
When determining the lateral boundary of the III belt, the terrain is taken into account: on a flat surface, the boundary passes at a distance of 500 m, and in the mountains - within 750-1000 m, depending on the slope of the surface.
The protective zone, which has a III belt, can significantly change its size by increasing the territory of the II or III zone, but it is necessary to purchase permits from the sanitary supervision.
The calculation of the WSS is carried out on the basis of data characterizing the territory of the well location and the characteristics of its surface wastewater.
Back to index
Necessary actions
Having made all the necessary calculations for the I belt, they begin its layout. To this end, the territory is landscaped, fenced and guarded. You can not plant trees in the zone, build up the site, apply fertilizers, pesticides, chemicals.
The sanitary protection zone in the 1st belt contains plumbing structures, which are equipped with equipment that excludes the possibility of water pollution through pipes and tanks. Special equipment is mounted on the well, which controls the flow and flow of water.
The protective zone, which has a second belt, must be freed from old, defective, unproductive wells that can pollute the aquifer. On the territory of the ZSO of the II belt, it is impossible to create new wells, drill and pump waste water.
In the region of the II belt, the use of artesian water for bathing is not allowed. Strictly prohibited in the territory where the protection zone passes, water pollution chemicals. If it is planned to drill a well, then it is produced on water horizons of coarse sand.
The protective zone involves the installation of wells, which must be reliable in all sanitary parameters. The boundary for the I belt has a size of 0.25 hectares, in view of the use of groundwater. It is possible to protect the entire territory of the I belt with a fence or green spaces.
Calculations are made on the basis of those options, the merits and errors of which are not determined without carrying out the corresponding work. The best one includes minimum costs to create a protective zone using advanced technical research, using modern technology and materials.