Thuja mining moth
T ya is more resistant to diseases than other conifers. Nevertheless, it is subject to various diseases, mainly of fungal origin. Some of them at high level injury is a serious danger. The causative agents of the most common thuja diseases have a wide organotropic specialization, that is, they affect trunks, branches, leaves, causing their death (necrosis). In addition, on all types of thuja it is known 7 types of insect pests. They damage scaly needles on shoots, wood of trunks and branches, and immature (green) cones.
Tui pests
Most thuja pests are oligophages and can develop on plant species from the cypress family: junipers, thujas and cypresses. They are found and harm mainly in the southern regions of the European part of Russia, in the Crimea and the Caucasus.
A few thuja pests belong to three ecological groups:
- sucking
- miners,
- xylophages.
Sucking pests
Thuja sucking pests suck juices from needles, shoots and immature cones. These include two types of coccids and one type of aphid.

Thuja false shield
The most harmful for thuja are juniper scale ( Carulaspis juniperus) and thuja false shield ( Parthenolecanium fletcheri) . In the juniper scale insect, the shield of the female is brown, elongated-oval, 1.9–2.0 mm long. This species is found in the southern regions of the European part of Russia, in Transcaucasia and Central Asia. In the thuja false scale, the body of the female is strongly convex, almost spherical, 3–3.5 mm long, yellowish-brown and brown in color. This false scale is found and harms in the parks of the European part of Russia, forests and parks of the Crimea, the Caucasus and Central Asia.
Much less often on thujas can be found thuja aphid ( Cinara juniperina) . This species belongs to monoecious non-migratory aphids. The integument of the body of the pest is grayish-brown, with a slight wax coating. Aphids feed on small colonies on the underside of 2–3 year old shoots. The needles on shoots damaged by aphids gradually turn yellow and eventually fall off. Thuja aphid is found everywhere.
Insects—miners
Miners are called insects, the larvae of which feed on the tissue of leaves or needles, making passages in the thickness of leaf blades or a growing shoot.
Scaly thuja leaves gnaw inside tiny caterpillars thuja mining moth ( Argyresthiathuiella) . The moves of the caterpillars are clearly visible when looking through the needles into the light. Damaged needles turn brown (turn yellow), and the tops of its shoots die off. After the exit of the caterpillar, well-marked small holes remain in the yellowed needles. The harm is minor. There is a thuja mining moth everywhere.

Damage from thuja mining moth
stem pests
Stem pests, or xylophagous insects, feed on bark, bast, and wood of branches and trunks. Most of them settle on strongly weakened and drying out plants. Three types of bark beetles are known on thujas: thuja beetle ( Phloeosinus thujae) , juniper beetle ( Phloeosinusaubei) , which can be found only in the forests and parks of the Crimea and the Caucasus.

Thuy beetle
Tui diseases
- Cabatine necrosis(pathogen - fungus Kabatinajuniperi)
Young shoots and leaves are affected, which turn yellow or acquire a reddish-brown color. On the rounded dying areas of the bark and leaves, sporulation of the pathogen is formed, which has the form of crowded black-brown rounded tubercles with a diameter of up to 0.3 mm, protruding from ruptures of integumentary tissues.
- Pestalocyopsis necrosis(pathogen - fungus Pestalotiopsisfunerea)
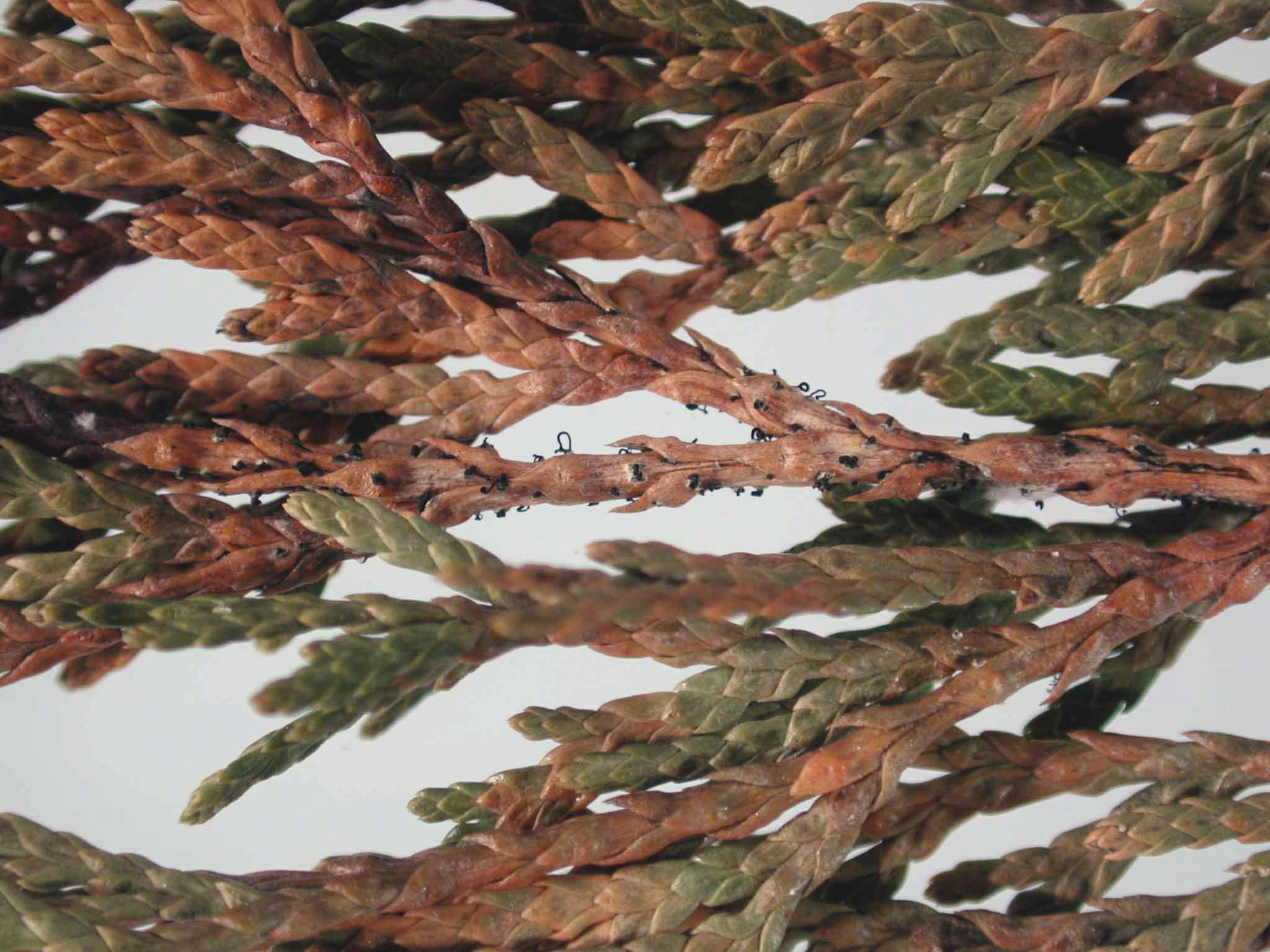

Pestalocyopsis necrosis
Young shoots and leaves are affected, acquiring a light brown or red-brown color. Leaf damage begins at the top of the shoots, spreading down. On dying and dead leaves and bark, sporulation of the fungus is formed in the form of a few scattered black rounded tubercles up to 0.2 mm in diameter, protruding from cracks in the integumentary tissues. Mature spores come to the surface of the affected leaves and shoots in the form of dark brown, almost black drops and thin strands, which are a characteristic sign of the disease.
- Phomopsis necrosis(pathogen - fungus Phomopsisjuniperovora)
Affected shoots and leaves turn brown. On the dead bark and in the axils of the leaves, sporulation of the pathogen is formed in the form of black rounded tubercles. Mature spores come to the surface of the affected organs in the form of light drops or strands.
- Cytospore necrosis, or osteoporosis (causative agents are fungi of the genusCytospora)
Mainly trunks and branches are affected, less often leaves that turn brown. The disease is detected by the sporulation of pathogens, which look like numerous, very small conical tubercles with dark tops. Mature spores come to the surface in the form of clearly visible golden yellow, orange or reddish drops, thin flagella and spirals. (More on the disease).
- Diplodian necrosis, or diplodia(pathogen - fungus Diplodiathujae)
The bark of trunks, branches and leaves is affected. The color of the bark almost does not change, and the leaves become brown or red-brown. On dead areas, sporulation of the pathogen is formed, which has the appearance of numerous scattered black rounded tubercles with a diameter of up to 0.5 mm.
- Brown Shutte (causative agent - mushroom Herpotrichiajuniperi)
The causative agent develops in winter under the snow, so the leaves of only that part of the crown that is in the snow cover zone in winter are affected. After the snow melts, the infected leaves are covered with a dense dark brown mycelium (mycelium), which, as it were, sticks together the affected shoots. On the mycelium, the fruiting bodies of the fungus are formed in the form of black spherical small tubercles, poorly distinguishable on the brown mycelium. Over time, the mycelium is destroyed, and dirty brown scraps remain on the affected leaves.
Mature thuja trees can become infected with wood-destroying fungi, of which the most dangerous are: autumn honey agaric ( Armillariamellea), root sponge ( Heterobasidionannosum), tinder fungus flat ( Ganodermalipsiense), tinder fungus Schweinitz ( Phaeolusschweinitzii) .
All these diseases occur, as a rule, against the background of a preliminary weakening of the thuja, caused by various unfavorable factors (weather conditions, an imbalance of nutrients in the soil, damage by pests, etc.).
Fighting methods
To protect the thuja from diseases, it is necessary to carry out a set of measures aimed at preventing and limiting their spread:
- use for planting plants that do not have signs of disease damage and damage on trunks and branches (mechanical wounds, insect damage, etc.);
- systematic monitoring of the condition of plants and the appearance of diseases during the growing season;
- creation of optimal conditions for the growth and development of thuja, increasing its resistance to diseases
- timely pruning and destruction of individual shrunken branches, which can be sources of infection;
- with a high level of infestation with necrotic diseases, preventive spraying during the growing season with copper-containing fungicides with strict adherence to application regulations.
_____________________________________________
Diseases and pests in thuja.
Thuja belongs to the cypress family, life forms vary from undersized shrubs to trees 15m high. Tui takes root perfectly in a variety of growing conditions (partial shade, bright sunny place, loam, sandy loam, urban conditions, etc.) It is difficult to tolerate the dry period, for this reason it is advisable to spray the plant in the evening in the summer (if there is an automatic watering system, then it is not necessary) . unpretentious plant with a variety of crown shapes from spherical to spreading has won sympathy all over the world. AT landscape design both small seedlings and large-sized 3-6 m plants are planted. Forming a regular plot style, evergreens harmonize perfectly both in their natural forms and are easy to cut. In single plantings, thuja already in adulthood creates complete landscape compositions. In addition to decorative thuja, it has medicinal properties, because with good humidity it releases essential oils into the air, which have phytoncides. As a rule, all plants require special attention after planting, for three years it gets sick, adapting to your site.
Tui pests.
False shield thuja- these are insects of small size, have a light yellow color, when an individual dies off, the larvae remain under a false shield (skin), from which the name came.
Signs of the disease: on the reverse side of the needles there are 3-5mm semicircular individuals. Tui begin to fade, the needles partially dry out, clearly standing out from the general view.
Twice a year in the spring in early May to mid-June, alternating after 7-12 days (depending on the weather) Komandor - Aktar - the last two times Champion fungicide. In autumn, it is better to apply Decis, mid-August to the end of September (every 2 weeks), the last treatment is also by the Champion.
spider mite- this insect is especially dangerous in hot summer periods, one female can endure up to 6 generations of larvae. It is the larvae that damage the needles.
Signs of the disease: the presence of abundant thin cobwebs on the shoots. Looking closely at the thuja scales, you can see many small yellow spots, and then brown dying areas. The damage done by the end of summer, beginning of autumn is especially visible.
Control and prevention methods: in hot weather, Aktofit can be used several times for prevention. If you find a disease, use Aktellik in the same period with an interval of 2 weeks, and additionally two times in 10-12 days Aktofit. In the spring of next year, at temperatures above +5 degrees, use Actellik 2-3 times with an interval of 2 weeks. To quickly restore color and improve growth, use top dressing for conifers, with the addition of sulfuric acid magnesium.
Aphid- These are gray insects with a slight sheen from a wax coating. They do not reach more than 3 mm, live in large colonies.
Signs of the disease: on the reverse side of the shoots one can see aphids arranged one after another. The needles turn yellow and eventually fall off.
Control and prevention methods: see the main methods of controlling aphids from common spruce. .
Mining Moth- This is a small insect, in adulthood up to 5 mm. Their life cycle is complex. In August-September, the caterpillar turns into a chrysalis. In the spring in mid-April to the end of May, butterflies fly. They lay their eggs in mid-June, forming "mines" in the leaf blade, which make it difficult to fight these insects.
Signs of the disease: in spring, partial dry top, needles partially turn brown and crumble. Mines are visible in the folds.
Control and prevention methods: From the beginning of April to the end of May, once every 10 days, treatment with Agrovertin. From mid-June to July, once every 3 weeks, shed with Ground Actara. End of August Processing several times on top of the crown with Aktara.
beetle- a pest of the root system of thuja. The name came from the sounds made during unexpected coups of the beetle. It is small 10-12mm, gray-brown in color. The danger is the larvae of this beetle, development takes place over 3 years. When they are small, they gnaw on thin roots, the older the individual, the larger the roots are damaged. Larva 25mm yellow-brown. Favorable conditions for their development are acidified soils and waterlogging.
Signs of the disease: Drying partial shoots. The needles are brightening. When digging, insects are visible.
Control and prevention methods: Periodically pour under the tree and around it with Grom-2 throughout the year. After eliminating insects, apply root stimulants and anti-stress preparations for plants.
Thuy beetle is a stem pest.
Signs of the disease: small holes on the bark, drying out of individual branches. Stem "flour" at the root system.
Control and prevention methods: now a good drug has appeared according to the description, I have been using it for the first year. Initiator. For prevention during the period of active flight of insects in the spring, at temperatures above +5, treatment with Aktara.
fungal diseases- there are many of them. You can distinguish signs of fungal disease from insect damage if you look closely at the plant. On the needles, the presence of dots, plaques, stripes, also on the bark of the tinder cap, rotting of the root is accompanied by drying of the shoots and needles from the tips.
Control and prevention methods:
Tui pests and methods of getting rid of themthuja aphid
These are gray-brown small insects living in a colony, similar to silver or white wax dust. If such pests have reached your thuja, then its needles will begin to turn yellow and fall off.
Fighting methods
The same insecticidal agents will help to save the thuja and stop the aphids as with the false shield. In addition, you can wash the affected areas with soapy water, covering the ground so that the soap does not reach the roots of the thuja. Such procedures should be done regularly every 7-10 days.
These two diseases are somewhat similar, so the treatment is the same. So, against thuya aphids and thuja false shields, trees can be sprayed with Fufanon insecticide. The norm of the drug is 10 ml / 10 l of water, the consumption of the working solution is up to 1.5 l / 10 m². Spraying with Fufanon is carried out from May to June, re-treating in the summer with extensive pest damage.
Aphids appear where there are ants. Check if there is an anthill on the site and have you noticed a large cluster of ants somewhere? The fact is that there is a food connection between aphids and ants. Ants feed on the secretions of aphids and protect them from predatory insects, as well as adverse weather conditions (aphids move to anthills for the winter). If you kill the ants, the aphids will also disappear. For these purposes, you can use the drug Anteater. The application rate is 1 ml / 10 l of liquid, the consumption of the working solution is 10 l / 5 m². The solution is applied to the soil in places of accumulation of ants during the growing season.
spider mite
This pest is especially dangerous for trees that grow on dry soil. By the end of summer, the number of damage increases, since the tick can produce about six generations during this period.
You can recognize it by the fact that the thuja needles are entangled in cobwebs and covered with yellow spots, as a result, they crumble.
How to fight?
At the first manifestation of a spider mite on your thuja, spray it with infusions of dandelion, garlic or colloidal sulfur. With a large lesion, acaricides will help. To prevent the disease, you can spray the tree cold water. This will increase the humidity and repel the tick.
Moth moth
Small larvae (their size is 4 millimeters) of this moth gnaw through tree branches. As a result, they turn brown, and the shoots die off.
Treatment
If you see traces of such larvae on your tree, it is possible to prevent their further destructive action by simple pruning. It will also help to stop the thuja moth by treating the thuja at the end of June with means (twice with an interval of eight days) that contain pyrethroids. For example, Fumitox Antiklesch, Tornado Antiklesch, Mosquitol Antiklesch.
Gray larch leaf roller
These dark caterpillars wrap the arborvitae needles with cobwebs, making cocoons. Pests are located in the middle of cocoons. Thuja from this loses its decorative appearance and may die over time.
Remedies from a leaflet
To prevent the appearance of a caterpillar, you need to spray with one of these drugs: Fufanon, Decis Profi, Aktellik. The norm of the last drug is 15-20 ml / 10 liters of liquid. Consumption of working solution - 1 l/10 m². Spraying with Aktellik is carried out in May - early June, repeated spraying - in the summer with a large number of pests.
Click Beetles
These root pests look like thirteen mm black or brown beetles. At first they feed on thin roots, humus. When the larvae grow up, they begin to feed on thick roots. As a result, the tree weakens, its development stops, the needles dry up and fall off. Especially often this pest is found in low areas where moisture stands.
breeding beetle
From the spread of click beetles, drainage, deoxidation of the soil, and digging of the earth in the fall help well. You can also add preparations with diazonin to the soil. For example, "Kapkan", "Bazudin", "Zemlin".
bark beetle
These little bugs burrow through tree bark and lay their eggs. The hatched larvae make their way in the same way. The tree usually dies within a month.
Fight against bark beetle
Unfortunately, no universal means of combating this pest has yet been invented. And since outbreaks of new foci of bark beetle lesions are recorded every summer, preventive treatments with Clipper are necessary.
Weakened thuja also need to be fed and treated with a growth regulator, the best of which for conifers is Zircon. It will help the trees to endure stress and recover faster. Spraying with Zircon of all trees is carried out once in the middle of the growing season (June-July): 0.3 ml / 3 l of water. Accordingly, the working fluid will need 3 l / 100 m². It is also necessary to use complex fertilizers marked "for conifers". For example, Reasil (Reasil), Bona Forte.
Outcome
Note that the timely noticed infection of the tree will help you cure it faster and prevent pest damage to the rest of the thuja. You should carefully and regularly inspect them so as not to start the disease. Having correctly identified the pest, you should immediately begin to remove it using the methods described above.
You may be interested in the information.
Thuja turns yellow - this is a problem that worries so many gardeners and owners of this coniferous plant. In many cases, after yellowing, the plant simply dies off, then nothing can be done. The reasons why thuja can turn yellow are quite problematic to establish.
But among the reasons there may be natural ones, because in the fall they turn yellow, since their life span has simply expired. It’s just that after a certain age, some branches begin to die off and it’s completely useless to worry about this, because the dead branch will definitely be replaced by a new, young one. This is a natural process that will not bring anything dangerous to the tree, but rather will renew the tree. This process occurs after three to four years of the life of the needles.
 Also, the color of thuja can change depending on the season. Some types of needles during the winter slightly change the color of the needles to yellowish, or slightly brown. This can be regarded as a protective reaction to frost and cooling. After winter, the needles will turn green with double strength and you won’t even remember that it was once yellow or brown. But it also happens that after the winter period it does not come into shape, but remains the same yellow, or darkened. In general, we can say for sure that a noticeably unhealthy tree will be immediately. By the way, in the spring there may still be such an option as a needle burn.
Also, the color of thuja can change depending on the season. Some types of needles during the winter slightly change the color of the needles to yellowish, or slightly brown. This can be regarded as a protective reaction to frost and cooling. After winter, the needles will turn green with double strength and you won’t even remember that it was once yellow or brown. But it also happens that after the winter period it does not come into shape, but remains the same yellow, or darkened. In general, we can say for sure that a noticeably unhealthy tree will be immediately. By the way, in the spring there may still be such an option as a needle burn.
If the needles turn yellow in the summer, then the reason may be in the care that is done incorrectly. You need to pay attention to the soil. Perhaps it does not have enough elements that are necessary for the enhanced growth of needles. Or maybe the soil just isn't right for her. Sandy soil, clay soil adversely affects it, if water stagnates on the site, then it is not surprising that the thuja simply turned yellow, because growth and development can be seriously impaired. It is also impossible for it to interact with animal urine, because it, as it were, burns it - at the points of contact, the thuja turns black.
Also, be sure to monitor watering, which should be regular and plentiful. It will somehow survive the increased humidity, but if it is not watered, then most likely it will turn yellow and dry out. On soil with high peat, the roots often rot and disappear. In the evening or in the morning, thuja can and should be sprayed. This will be like a breath of fresh air for her, because spraying is an integral part of the active development of the plant.
By the way, treating with an antifungal agent will not be harmful at all, but for prevention this is the very thing, because it is better to prevent the appearance of a problem than to solve it later.
If the thuja is already drying up and you understand that these are the consequences of a drought, then you need to act this very second. First you need to cut dry branches so that the plant is cleansed and renewed. Fear not, because this plant can tolerate pruning very well. Then you need to remove the point, which is called growth - that is, the top of the needles needs to be cut off by about ten to fifteen centimeters. The plant on the soil must be fertilized with acidic peat, that is, a thick layer should cover the soil, mix with a layer of top soil. Then follow this with a fertilizer that is specially designed for coniferous plants. There is such a remedy as "Epin" - so they need to spray the tree, after ten days have passed, they need to make such a remedy as "Zircon", it must also be applied by spraying. And after another ten days, you need to spray it with such a tool as mullein.
These resuscitation actions must be carried out before the end of June, that's for sure, otherwise the plant simply cannot be saved. Already before the end of the summer you will be able to observe a real revival, there will be no trace of a sick thuja. And next spring, you simply won’t recognize it - a completely renewed, fragrant thuja will give you beauty and comfort on the site.
In general, thuya is ornamental plant which should always look good. If it turned yellow, in any case, the jamb of the owner. After all, yellowness can depend on many factors, mainly questions about caring for it. If the thuja turned yellow in the summer, then most likely this matter concerns drought. In this case, it is impossible to postpone, if the thuja can be saved, then this must be done immediately and on the same day. AT general action not complicated, and if you do everything right, you will quickly bring the thuja back to life. But be warned that recovery can take a long time. If you see that all is not yet lost, then do not despair. The main thing is to follow the rules for care and everything will be fine.
 If the needles turn yellow and fall off, then, most likely, it is damaged by thuja aphid, thereby reducing the decorativeness of plantings. These insects have a gray-brown color, and they are also covered with silver-white wax dust. Aphids damage mainly the lower part of the shoots. To get rid of them, you need to spray the plant with karbofos.
If the needles turn yellow and fall off, then, most likely, it is damaged by thuja aphid, thereby reducing the decorativeness of plantings. These insects have a gray-brown color, and they are also covered with silver-white wax dust. Aphids damage mainly the lower part of the shoots. To get rid of them, you need to spray the plant with karbofos.
- Karbofos;
- Aktellik.
Processing is carried out before bud break during a mass outing of vagrants.
Wireworm larvae most often found in low-lying areas with acidic soil and stagnant water, since these are the conditions that are most favorable for them. It will help to get rid of such pests by drainage and deoxidation of the earth, as well as autumn digging. If a large number of beetles is observed, then agents containing diazonin are introduced into the soil.
But if a coniferous plant was damaged by a thuja beetle, then it should be disposed of immediately so that other thuja do not suffer. When this pest infects thuja, it leaves holes in the bark. Therefore, when planting healthy trees, it is necessary to carefully inspect them for the presence of passages in the trunk and resin leakage. Moreover, it is necessary to provide the best conditions for the development of strong and healthy plants.
What diseases affect thuja?
Phytophthora
 This fungal disease is the most dangerous. It strikes the root first, and then destroys the top layer of a coniferous plant. This is reflected in the thuja as follows:
This fungal disease is the most dangerous. It strikes the root first, and then destroys the top layer of a coniferous plant. This is reflected in the thuja as follows:
- The tree begins to wither;
- A gray color appears;
- The trunk from below becomes soft.
But under the bark, the tissue changes its color, it becomes brown, while a plaque appears below. The root smells of rot, besides, it becomes brittle.
As a rule, this disease affects thujas growing in a place where moisture constantly stagnates or the soil is not drained. To prevent the appearance of phytophthora, it is necessary to water the plant with fungicides as often as possible. However, if the disease still managed to get to him, it is better to get rid of the thuja, and change the land, since such a fungus is able to live in it for a long time.
brown shoots
A similar disease occurs mainly in early spring. It manifests itself by yellowing of some scales. If nothing is done, then the shoot will first turn brown, and then die. For treatment, it is necessary to cut out the affected processes. After that, the tree must be constantly sprinkled with limestone and fed. From mid-summer to the end of September, thuja should be sprayed with foundationazole.
By the way, browning and yellowing of the tops of the plant can occur when there is a violation of the access of nutrients from the roots to the crown. This happens for the following reasons:
Fusarium or tracheomycosis. In this situation, it is necessary to water under the root and spray the thuja crowns with a 0.2% solution of foundationol. Instead, you can use another fungicide, for example, Abiga Peak, Kartocide or HOM. It will also help save thuja treatment with zircon, which improves the ability to resist fungal diseases.
Root locking. It usually occurs due to too high standing of groundwater.
Rust and Shutte
 These fungal infections are manifested by abscission and darkening of the needles. Most often, infection occurs in the spring, but spreads year-round. As a rule, young plants suffer from them. For prevention, you need to cut off all bad branches and burn them to prevent spread to other coniferous trees. True, this technique does not always help.
These fungal infections are manifested by abscission and darkening of the needles. Most often, infection occurs in the spring, but spreads year-round. As a rule, young plants suffer from them. For prevention, you need to cut off all bad branches and burn them to prevent spread to other coniferous trees. True, this technique does not always help.
It is advisable to process the affected thuja copper fungicide, such as HOM. Approximately 40 grams of this powder should be diluted in 10 liters of water. The affected plants are sprayed with the finished solution in May and summer, when the disease reappears. But preventive treatment must also be carried out on the rest of the thujas, without exception, because they are all susceptible to infection with rust and shute. Make it the same drug, but only once in the spring.
If it is not possible to achieve the desired result, then it is better to shed the trunk circles of infected plants with Fundazol. Moreover, this drug should not be sprayed with thuja. It is used exclusively for the destruction of infection in the soil.
For the treatment of a plant affected by shute, use Topsin-M. To prepare the solution, you will need to take the drug 15 grams, and dilute it in 10 liters of water. Enough mixture to spray one mature tree. Processing is carried out once in the spring, when the night frosts stop.
You can replace HOM with Borodskaya mixture. This tool is proven and very effective.
Strengthening the immunity of thuja top dressing
The appearance and condition of most trees depend on the balance of nutrients and their availability. With a lack of iron in the ground, the needles turn white and turn yellow on individual shoots, and with a lack of phosphorus, they acquire a red-violet color. If there is little nitrogen in the soil, then the plants begin to grow worse.
That is why it is necessary to perform foliar and root feeding. For these purposes, special fertilizers for conifers are used. Plant resistance to care errors and negative factors increase biologically active drugs and growth regulators. Many gardeners, in order to strengthen immunity to water or temperature stress, improve seedling survival and nutrient intake, use the following tools:
- Nikfan;
- Zircon;
- Humisol;
- Immunocytophyte;
- Epin-extra.
In summer, in the heat, the root circle of the plant is desirable cover with peat. Thus, moisture loss can be avoided. In addition, it should be covered from sunburn, as rot may appear. Water the tree occasionally from above to stimulate the development of young shoots.
In the first few winters, sawdust is used to powder the earth. But in the spring, thuja must be fed with fertilizers for coniferous trees. In addition, experts recommend using organic and mineral substances: biohumus, ash or compost.
After planting the thuja, it is advisable to dilute the fertilizer by half to minimize the risk of burns. In the spring you need to cut the plant and remove diseased growths. Shorten shoots by 30% several times a year to give them splendor and stimulate branch growth. With proper care of the plant, pests and diseases will bypass it, and the site will be decorated with a healthy and beautiful thuja.