The construction of a private house, as well as its design, carried out in accordance with the requirements of regulatory regulatory and technical documentation, is the biggest resource for saving costs!
Since, firstly, in compliance with the standards and technical regulations, you reduce to a minimum the possibility of making construction errors, the correction of which always amounts to many thousands of rubles. Secondly, a lot of marriages made during the construction of a house can only be revealed during its operation. Alterations of building structures during residence cause the greatest inconvenience and force them to bear impressive unplanned expenses. For example: a damp wall, a leaking roof, overheating electrical wiring, an icy floor, etc.
If you want to achieve maximum savings, then you need to competently control the progress of construction work. To do this, you need to know the key control points and quality assessment criteria. This section contains a brief selection of the main regulatory documents required for the design and construction of a private house.
1. Design, preparation for building a house
1.1. Architectural, general construction standards.
First you should familiarize yourself with the Code of Design Rules SP 11-III-99. After reviewing this document, you will definitely know what papers are required to start construction on your individual site. During the construction of a residential building and various outbuildings, there are norms for their location on the site, according to the following documents:
- "Urban Planning Code of the Russian Federation" dated December 29, 2004 N 190-FZ;
- "Planning and development of horticultural associations of citizens, buildings and structures" SNiP 30-02-97;
- "Residential buildings" SNiP 2.08.01-89 * and SP II 106-97;
- "Single-apartment residential houses" SNiP 31-02-2001;
- Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements "SNiP 2.07.01-89;


This is how the approximate layout of buildings on the site looks like according to RSN 70-88.
Having carefully studied RSN 70-88 (republican building codes), SNiP 31-02-2001 and SNiP 2.08.01-89 (Building Norms and Rules), you will find out what are the restrictions on the area and height of the premises of a residential building.
There are minimum restrictions on the height of floors (SNiP 2.08.01-89). The house may be declared unsuitable for permanent residence if the height of the residential floors is below 2.5 m from floor to ceiling. In the attic floor, the height norm is from 2.3 m. The number of storeys of the house is usually determined by the above-ground floors, which includes the attic floor. It is not allowed to place living rooms in the basement or basement floor. The basement floor can be equated to the above-ground floors if the top of its ceiling is at least 2 meters above the ground level. If it is decided to place utility rooms in the basement or basement floor, then the height from floor to ceiling must be at least 2 meters.
The area of a residential building is defined as the sum of the areas of all rooms on the floors. Balconies and loggias are also included in the total area. The area of stairwells at the level of a given floor is considered.
If you plan to build a house on the territory of a garden partnership, then you must definitely take into account the requirements of SNiP 30-02-97 "Planning and development of gardening associations of citizens, buildings and structures" as amended in 2011.
1.2. Concrete structures.
1.3. Thermal engineering standards. Resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures.
1.4. Engineering Communication.

Electric wires from the street pole to the entrance to the residential building must run at a height of at least 2.75 m from the ground. If the withdrawal is carried out on the other side of the street along which the vehicle is moving, then the permitted height is 6m. The length of the branch from the main line to the residential building should not exceed 25 m, if it turns out more, an additional support is installed. All points of contact of the cable with the surface of the building, and passing through the walls, must be fireproof and reliably insulated, and at the points of entry, the outer end of the insulating pipe must look down to prevent atmospheric precipitation from entering there.
In case of violation of the rules for installing sewer networks, the developer is threatened with their regular clogging. He is doomed to frequent cleaning of pipes clogged with drains. According to the standards, the daily sewage costs per person are about 200 liters. The smallest diameter of the external sewer pipe must be 100 mm, with a slope to the common collector of at least 8%. The smallest depth of the pipe in the ground is 0.3 meters. If there is no centralized street sewerage, then it is allowed to build filter wells and trenches with the obligatory installation of a septic tank in front of them (industrial treatment device). The base of artificial filters should be 1 meter above the groundwater level.
If you have the appropriate knowledge and experience, it is allowed to independently install engineering networks, with the exception of gas communications. There are very stringent requirements for the acceptance of a gas supply system. Only a specialized organization has the right to install a gas pipeline and connect gas appliances.
Gas pipes can be introduced into a residential building only from the side of the furnace or kitchen. If the house is old and has a heating stove, then it is allowed to enter communication into the living room, provided that the disconnecting device is placed outside the building. In no case should the gas pipe be introduced into the house through the foundation or under it. If the pipe is laid along the outer wall of the house, then its conditional diameter should not exceed 50 mm. It is not allowed to arrange detachable connections of the pipeline under window openings and balconies. In general, all connections must be welded, threaded connections - only at the installation sites of valves and gas appliances. If the gas pipe, according to the project, passes over footpaths, then it should be fixed at a height of at least 2.2 meters from the ground.
It is not allowed to install more than two heaters in one room. It is strictly forbidden to install a water heater in the bathroom, otherwise you can get a wonderful gas chamber.
The room for the gas boiler and water heater must be at least 2 meters high. When installing one device, the room has a volume of at least 7.5 cubic meters, and with two devices - at least 13.5 cubic meters.
2. Building a house.
2.1. Foundations and concrete structures
2.1.10. The rest of the necessary information for the construction of the foundation can be found in: SNiP 2.02.01-83; SNiP 31-02; SNiP 2.02.03-85; SNiP 2.02.04-88; SNiP 2.02.01.
2.2. The walls of the house.
2.2.18. GOST 24454-80 - Softwood lumber, GOST 9685-61 - Softwood blanks.
No law contains direct guidance on respecting the distance between adjacent buildings, but the current codes and regulations for building contain clear guidelines on the issue, let's look at them.
Where to start building
Buy a plot for building. The rules of IZHS allow the construction of buildings for living and household needs. The permit is issued by the administration of the place of residence. Documents will be required from the developer, among them for the ownership of the site and the design of the planned buildings. The developer must first familiarize himself with the rules of construction.
Among other papers, it is required to have a town-planning plan, which will allow obtaining permission for and commissioning. The document is for informational purposes only and does not confirm ownership of the land. But for obtaining it is necessary to provide a number of documents on ownership. Among the multitude of information, urban planning plans reflect what is important for the developer.
A number of documents regulate construction, define general rules and special norms related to sanitation and fire safety. General issues are reflected in the design and construction rules. In practice, building codes and regulations (SNiP) are used. Separately, there are SNiPs for private developers and gardening associations. Sanitary standards are reflected in the SanPin, fire safety - in the NPB.
In order to choose the right place for buildings, they determine the distance to neighbors, find out the material of the erected structures. This data will help calculate the distance to a neighbor's house, a fence, and the placement of other buildings. Measurements between objects are carried out in a straight line. The clearance between the houses does not matter if the buildings are located deep into the site or closer to the road. So achieve that the buildings were not on the same line.
Land allotment planning
To rationally place buildings, draw up a plan. Options for the location of the house, garden, vegetable garden, flower beds, outbuildings are selected. You can take as a basis a suitable sample from the Internet or magazines. It is necessary to provide for the use of each piece of land with the maximum benefit. Any option must take into account sanitary and fire regulations.
First, determine the boundaries of the site in kind, choose a place for the house. It is built only where permitted by the rules. The distance to the point of contact between the plots, the neighbor's dwelling and to the conditional line between the plot and the road is taken into account. In addition to the house, various other buildings are located on the site. You can also arrange a place for composting waste and a yard toilet.
It is the toilet, compost pit, local sewerage that often cause conflict with neighbors. When placing them, it is necessary to observe the distances prescribed by the rules from your own house and the neighboring plot. The preliminary plan provides for the fulfillment of all requirements, divides the site into zones: residential, recreation, gardening, economic.
Unconditional compliance with fire regulations
The distance between objects is determined primarily by fire safety requirements. Dense buildings, unacceptably small distances are the cause of massive fires, when fire from one building is transferred to another. Also, firefighters must have unhindered access to the source of ignition.

To determine the minimum required gap between buildings, the material used in the construction of nearby houses is taken into account:
- 1. The house was built of brick, stone, concrete. Permissible interval is 6 m if the neighbor has applied a similar material.
- 2. Wooden elements and non-combustible materials are used. To houses of the same type, the required distance is 8 meters.
- 3. Wooden buildings. The distance to neighboring dwellings is 15 m, even if the wood is treated with a fire-fighting solution.
The distance between neighboring houses, from the fence to other buildings, others are measured according to the rules: building elements protruding beyond half a meter are taken into account. If they protrude less, measure from the plinth or wall.
Sanitary requirements for construction
Sanitary standards determine the smallest distance from a residential building and buildings to a fence between sites. Regardless of the height of the fence, the building should not be located close to it. A minimum distance of 3 m must be observed. By agreement with neighbors, it is possible to build closer if the fire distance is observed.

Smaller outbuildings can be as little as 1 meter from the fence. This norm does not apply to buildings for breeding poultry and livestock, greenhouses. They are located 4 meters from the fence. A compost pit, a yard toilet are removed from the border between allotments by 8 meters.
Sanitary regulations also stipulate the planting of trees, which most often causes disputes between neighbors. However, the neighbor has the right to make claims if the norms for the location of buildings on the site are not met. Tall trees are planted 3 meters from the fence, of medium height - 2. Shrubs - 1 meter from the neighboring allotment.
How to make a fence
SNiP defines the requirements for the fence between sites. Their observance is simple, for the most part these are recommendations. The permissible height of the fence is not higher than 0.75 m. It is possible to increase the height to 1.5 meters, but then the upper half is made of transparent material. This will protect the neighbor's area from shading. It is forbidden to use one of the walls of outbuildings, a garage as a fence.

If it is possible to agree with a neighbor on a fence of a greater height than the standards indicate or on a blank fence, the rules are allowed to be violated. The agreement is valid for 3 years, during which time it can be appealed if it is concluded orally. To protect yourself from surprises, it is better to conclude a written agreement that cannot be challenged in court.
If the land passes into the possession of another person, any agreement concluded with the previous owner becomes invalid.
Consequences of non-compliance with building rules
Even with the absolute compliance of the construction with all the rules, it is impossible to fully protect yourself from the claims of the neighbors after the completion of the work. It is desirable to coordinate the placement of all structures on the site with the neighbors, to allow the development plan of the land plot to be studied and the agreement to be signed. In this case, if relations deteriorate for some reason, a conflict arises with a neighbor, he will not be able to appeal the written agreement.
The contract cannot violate fire safety. Other issues regarding any object can be resolved, mutual understanding can be found. Violation of certain rules does not lead to the imposition of penalties, but the dissatisfied party has the right to go to court. Owners who violate construction requirements may be held administratively liable.
If a peaceful solution to the conflict failed, it is possible to appeal to the administration, a lawsuit. The fastest and most effective way is to contact the prosecutor's office to check the norms for building a private house from neighbors. The presence of evidence will speed up the consideration of the application. For example, a neighbor violated sanitary rules, which caused harm: evidence can be a photo of sewage, water analysis in a well.
Building a house on your own plot is a rather bold decision. At the same time, the norms for the construction of a private house should be observed in terms of distance to someone else's site, and the height of the fence should also correspond to the number of storeys of the planned house.
What do you need to know before building a house? First of all, you need to comply with building rules and regulations. For long-term and safe operation, SNiPs are required for both yours and your neighbor's house. Compliance with regulations will ensure fire safety and comfort.
Construction and site planning
The documents must be correctly drawn up and there must be a certificate of ownership of the land on hand. Planning begins with the designation of boundaries - separation by a fence. Building codes are based on fire safety planning. Do not direct roof runoff of rainwater to an adjacent area of 1 meter. Water is supplied autonomously or centrally. Heating comes from autonomous systems (furnaces, boilers). A compost pit should be installed if there is no sewerage. Gas supply is made from reservoir sources, gas networks or from gas-balloon installations. After completion of all work, documents for real estate should be issued.
Distance between houses and other objects
To ensure fire safety, the location of buildings relative to each other is regulated by SNiP. It contains the planning rules and norms for building. The distance that is required when creating the project itself is what you need to focus on. It is a guarantor of fire safety, because when a fire ignites from one building to another, the fire quickly spreads.
Minimum fire distances:
- non-combustible materials (brick, concrete) - 6 meters
- combustible materials (metal with wooden rafters) - 8 meters
- wood - 15 meters
If the layout of the house is designed for 2 owners, then the distance is measured along one line between the buildings.
Distance to the fence
- the distance between the neighbor's plot and the house - 3 meters
- shed for poultry, livestock, animals - 4m
- shower, baths, toilet - 3m
- garage - 1 meter
- greenhouses - 4 meters
Requirements and procedure for the fence

Types of fences
- panel boards - boards are arranged horizontally or vertically (pine or spruce is the best wood)
- picket fence - planks (vertical) are attached to the bars, there can be different heights
- trellises - wooden slats connected into diamond-shaped or square cells
- palisade - fragile in itself
Rules for the location of the house on the site
Before you start building a cottage or house, you need to study building codes. This is necessary in order to avoid unpleasant consequences. If the standards are not met, then, most likely, the building will have to be demolished.
Studying documentation
- standards for placement on a land plot of a house (SP 30-102-99 for individual and low-rise construction; SNiP 30-02-96 for the construction of summer cottages and soda buildings; SNiP 21-01-97 fire safety)
- develop a normative master plan
- obtaining a topographic image - it shows buildings and neighboring residential buildings
The norms of individual dwellings provided for by the buildings of the site
SNiPs are designed to make buildings as comfortable and safe as possible. In SNiP 30−102−99, the standards for low-rise housing developments are prescribed. In addition to the house, on a similar site, there may be outbuildings, perennial plantings, underground communications. Such facilities are regulated by fire and sanitary standards. Consider the relative position and distance of objects. So that in the future there are no troubles in the arrangement and construction of the site, it is necessary to comply with the norms of izhs.
"Red line" - this term means the line separating the common areas from the building area (roads, highways, driveways).
Obtaining a building permit

Rules to be observed during the construction of izhs
IZHS by itself means the construction of low-rise buildings intended not only for buildings, but also for storing food and materials, raising livestock.
Rules
- convenient location close to the road
- conducted and working communications
- infrastructure developed in the area
Fertile soil, development of the area and remoteness from the industrial zone are an important condition for the construction.
Subject to the rules, construction can begin on the condition that:
- Permission has been obtained for the construction of the building and there is relevant documentation
- Documents have been checked more than once, among which there is a plan with the boundaries of the plots
Other buildings are possible on the territory
- sheds
- dry closets
- compost pits
Norms for individual housing construction

The main rules of SNiP for construction in the residential private sector
To clarify the place of construction of the house, you need to contact the authorities (administration) for help. There you can find all the norms for building on an individual request. You can not build too close or close, there must be a certain indent between the sections. There is no law on the location of buildings on a private plot. There are building rules for a garden partnership. They indicate the distance from the house to other sites and so on. You will risk your own safety if you do not follow the rules. You may also be sued in court and may be required to pay a fine and change the location of the house. To avoid this incident, it is worth finding out exactly how many meters should be from the building to other houses.
What are the dangers of non-compliance
It will be necessary to correct sanitary standards, resolve all issues that have arisen with neighbors and assure written consent. The Code of Administrative Offenses defines penalties for non-compliance with the norms for the placement of buildings. The fines are huge.
Basic rules for the construction of an individual residential building SNiP
 You should understand the documents for the land and mark the boundaries with neighboring lands. The cottage must be located no closer than 3 m from the streets and 5 m from the roads. Outbuildings should be located away from the street, in the depths of the site. Distance of at least 4 m from buildings. The distance from the outbuildings and the house to the neighboring plot is measured as a hotel (at least 3 m). The distance from the forest to the house is at least 15 m.
You should understand the documents for the land and mark the boundaries with neighboring lands. The cottage must be located no closer than 3 m from the streets and 5 m from the roads. Outbuildings should be located away from the street, in the depths of the site. Distance of at least 4 m from buildings. The distance from the outbuildings and the house to the neighboring plot is measured as a hotel (at least 3 m). The distance from the forest to the house is at least 15 m.
Regulations for the construction of a house on a land plot izhs
Individual construction is the area of residential land that is provided for acquisition in order to:
- growing berries, fruit and agricultural crops
- recreation
- the buildings
House status from land area:
- cottage, garden house
- country house
- individual house
It is necessary to follow the rules of construction for the correct and effective zoning of your own land area. It is necessary to correctly divide the plots into zones for the construction of building facilities on them.
Division into types:
- horticultural zone - garden, greenhouse, garden, greenhouses, shrubs
- backyard area - summer kitchen, garage, sauna, cellar, shower, toilet, workshop, well
- recreation area - swimming pool, playground, gazebo, sheds, flower beds
- living area - guest
Sanitary standards:
- from outbuildings - 50 meters
- from the garbage collector - 15 meters
- from the well - 8 meters
- from the septic tank - 3 meters
Indicators for the construction of a private house from neighbors
 For fire safety, the distance of the house on the adjoining sites must be at least 6 (brick) -15 (wood) m. A fence specified in the project is placed around the site. There should be special facilities for breeding animals. The distance from the buildings to the trees is 5 meters. Closer than 4 meters to power grids and underground utilities 1.5 m cannot be located. For shrubs from buildings 1.5 m and up to the selected boundaries of the site 1 meter.
For fire safety, the distance of the house on the adjoining sites must be at least 6 (brick) -15 (wood) m. A fence specified in the project is placed around the site. There should be special facilities for breeding animals. The distance from the buildings to the trees is 5 meters. Closer than 4 meters to power grids and underground utilities 1.5 m cannot be located. For shrubs from buildings 1.5 m and up to the selected boundaries of the site 1 meter.
On the plots allotted for individual housing construction, the construction of private houses, cottages, baths, outbuildings, and so on is allowed. However, despite the fact that the land plots are owned, the statement “my land, I do what I want” does not apply to them.
The norms for building a house on the IZHS site in the relevant sectors are quite strictly regulated by SNiP. The documentation indicates the norms for indents from fences, neighboring houses, the red line, the location of objects on the site, and so on. To obtain a building permit, you must provide a plan that will fully comply with SNiP.
Distance between houses and other objects
The distances and location of outbuildings relative to each other are regulated by SNiP 30-02-97 to ensure fire safety. It describes the norms and rules for location and planning in the development of the private sector and horticultural associations. The first thing you need to pay attention to when creating a project is the required distance between the houses.
Much attention is paid to this item in the licensing authorities, as it guarantees fire safety. The fact is that when ignited, the fire quickly spreads from one building to another. When building a residential facility, it must be borne in mind that the distance is calculated not from the fence, but from the neighboring house.
The distance depends on the degree of fire resistance of the materials used:
- if non-combustible materials (brick, concrete) are used in the construction of a residential facility, then the distance is 6 m;
- if combustible materials for floors are used during construction (metal frame with wooden rafters), then a distance of 8 m is required;
- if the cottages are built of wood, then the distance should be 15m.
The exception is the two-row layout. It is also permissible to build two objects side by side if the “1 house for 2 owners” system is used. The distance between buildings is always measured strictly in a straight line, bends and corners are not taken into account.
From house to barn
SNiP does not regulate fire distances for the location of buildings on the site. However, it contains sanitary norms and rules for the arrangement of economic facilities. They are more advisory in nature, so minor errors are allowed. However, when selling a land plot in the private sector, problems may arise if these standards are not met.

Distances are considered from the outer wall of the house in a straight line. It is necessary to locate all outbuildings in the sector, taking into account the following recommendations:
- outdoor toilet at a distance of 12-15m from the house;
- to the bath - 8m, the same applies to showers;
- to sheds with cattle and poultry - 12-15m;
- to the compost pit - at least 8m;
- the minimum distance of household objects from the house is 4m;
- it is allowed to arrange a garage inside a residential facility.
The location of buildings relative to each other is also regulated. So, the compost pit and the well should be at a distance of 20m from each other. This is due to the fact that there is a high risk of toxins and other harmful substances getting deep into the soil, from where they can be transferred to drinking water. You can not put a well next to the fence.
Also, for hygiene reasons, it is recommended to keep a well and a toilet at a considerable distance so that drains do not get into the water. At the same time, the location of the artesian well is not regulated, but it is better to adhere to the above rules, especially if the water is shallow.
Fire safety requirements for the arrangement of baths are very strict, since they are built mainly from wood. At the same time, wood-burning stoves are used inside, which creates an increased risk of fire. The distance from the neighbor's house to the bath must be at least 8m.
Since 2015, SNiP also applies to the location of the garage. The minimum distance from the fence is 1m, and from the neighboring area - 6m. The garage should be located at a distance from the residential building, unless it is equipped on the ground floor. In this case, additional ventilation will be required.

Distance to the fence
SNiP pays great attention to the distance between buildings and fences. This is also more of a hygienic consideration than a fire safety requirement, as being too close to a neighboring property can cause increased shading. This is not always acceptable. So, in SNiP the following norms are indicated:
- the minimum distance between the house and the neighboring plot is 3m. If the distance is reduced, a document confirming the consent of the parties must be drawn up;
- a barn for animals, poultry, livestock should be located at a distance of 4m from the fence;
- sanitary facilities (baths, showers, toilets) at a distance of 2.5 - 3.5 m;
- when installing a greenhouse, the recommended distance is 4m, this will avoid both shading and the ingress of wastewater with fertilizers into the neighboring area;
- for a garage and a shed with inventory, the minimum distance is 1m;
- the optimal distance for the construction of any buildings is 3 m from the fence. This will allow not to obscure the neighboring area, as well as to avoid conflicts due to the possible penetration of sewage over the fence.
When building a bath, it is better to equip it with an additional drain; for this, it is necessary to equip a sewer or gutter.

Placement of trees on the site
Special attention is paid to the placement of trees and shrubs along the fence. Green spaces can create unnecessary shade in the neighboring area. However, the neighbor's claims can only matter if the tree is not planted in accordance with SNiP. The distance from the tree to the fence is measured from the center of the trunk. How should green spaces be placed on the land:
- bushes at a distance of 1m from the fence;
- medium-sized trees - 2m;
- tall - 4m.
When planting seedlings, it is necessary to consider how they will grow in a few years.
What should be the fence
SNiP imposes some requirements on the fences themselves. For the most part, they are advisory in nature, and it is not difficult to comply with them.
Fencing between land plots should not exceed 1.5 m in height. At the same time, it can be continuous only up to the middle. Otherwise, the neighbor may complain about the excessive shading of the site.
The choice of fence material remains with the owner of the site; there are no recommendations in the regulatory documents regarding this. It can be a chain-link mesh, trellis or even a palisade.

The height of the outer fence is not regulated. However, if this figure exceeds 2m, additional approval may be required. The external fence can be solid, for example, from a profiled sheet.
If you manage to negotiate with your neighbors, then you can put up any fence, even a solid one and 3m high. The most important thing is to draw up a document confirming the agreement with the owner of the adjacent plot.
Requirements for individual housing construction
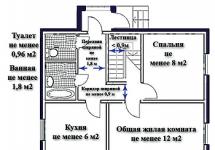
SNiPs regulate not only the location of buildings on sites, relative to each other, but also the size of the buildings themselves. The normative documents detail the minimum dimensions of residential premises:
- the common room (often called the living room) must have an area of 12 sq.m;
- each bedroom - from 8 sq.m;
- the minimum size of kitchens is from 6 sq.m.;
- bathroom - from 1.8 sq.m;
- entrance hall - also 1.8 sq.m;
- toilet about 1 sq.m;
- ceiling height - from 2.5 m.

Anticipating the desire of owners and developers to save space, the SNiPs also contain standards for passageways. This ensures compliance with sanitary standards, and also ensures the safety of residents. The width of stairs and corridors must be at least 0.9 m. The dimensions given are the minimum.
For the attic floors, a reduction in the square is provided. For example, bedrooms can be 1 sq.m. less. Normative documents impose restrictions on the use of basements and basements. Living quarters may not be located below ground level. If it is planned to use the basement for economic purposes, then its height must be at least 2m.
Communications
The dwelling house should be provided with minimum amenities. Communications must be connected to the object. Or you need to provide their analogues.
For the arrangement of sewage, it is allowed not only to use pipes and connect to the central collector, but also to arrange cesspools. At the same time, it is necessary to provide filters and methods for cleaning toilets.
Each owner solves the issue of heating independently. It can be a stove or a gas boiler. A system of radiators and convectors can be used. The norm is a heat flux of 10 W per 1 sq.m. The minimum size of the boiler room is 5 sq.m. You can also connect to the central heating system, if possible.

Opening windows are enough to ventilate the rooms. Also, glass should provide an optimal level of lighting. If there is no fresh air supply in the bathroom and toilet, it is necessary to equip ventilation.
If a gas connection is provided, the pipeline can only be laid from the side of the boiler or kitchen. Pulling gas through the entire house to the place of use is prohibited. The exception is the case when a stopcock is installed at the entrance to the room. The gas pipeline cannot be pulled through the foundation. Connections must be welded, threaded inserts are also acceptable.
When using gas cylinders, safety precautions must be observed. The volume of the cylinder should not exceed 12 liters. If they are larger, then they must be kept in a separate room in metal boxes, outside the living quarters.
Electricity is most often supplied by overhead power lines. In this case, the wires should not interfere on the roadway. The minimum height at which the cable must be laid is 2.75m if there is no active traffic on the street. If the power line passes through busy streets where cars drive and people walk, then the wire must be at a height of at least 6 m so as not to interfere with traffic and not create a threat.
Supports for power lines should be located at a distance of no more than 25m from each other. If the house is located at a greater distance, then an additional pole must be installed. The wires are attached at a distance of 20 cm from each other. In the house or outside it, metering devices for consumed energy (electricity meters) are installed in special boxes. Inside the room, wiring is installed using insulating materials.

Do not forget about water supply. You can connect to the central system using plastic or metal water pipes. Artesian wells, water pumping stations, wells on the site are also often used. Another option is drinking water supply. The issue with hot water is solved by installing a boiler.
fire safety requirements
In SNiPs, fire safety requirements are not singled out in a separate chapter. They are complex in nature and are present in each section. One of the fire safety rules is the placement of buildings at a certain distance from each other. An important role will be played by the material of construction.
Another fire-fighting rule is the use of refractory materials for finishing and strengthening the building. Good communications also ensure fire safety: it is necessary to regularly check the condition of wiring, gas pipes and connections, electrical appliances, and so on.
If fire safety requirements are violated, it is likely that the house will not be allowed to be put into operation or even obligated to be demolished.
Building norms relative to the red line
This is another not very clear section in SNiPs. Not everyone knows and understands what lies behind the concept of the red line.
The red line is a conditional border, a line passing between the site and the roadway, separating them from each other. Often it is on it that a fence is installed. So, the red line separates the building area from the adjacent area.

During construction, the location of the red line must be taken into account. Buildings are placed with this trait in mind. So, one of the requirements of SNiP is the placement of a residential building at a distance of 5 m from the red line. Buildings should not protrude beyond it, and some should be at a considerable distance.
If this requirement is violated, the court may order the demolition of the building protruding beyond the red line. Also, neglect can result in a fine. So, when planning and building, it must be remembered that objects should not protrude beyond the red line.
Required documents
It is impossible to arbitrarily start building in the residential sector. You need to get permission. And for this you need to correctly draw up a plan, taking into account all sanitary and fire safety requirements and rules. On land plots in the residential sector of the city, building is allowed for private houses, not higher than 3 floors, placement of outbuildings, baths.
First of all, you need to choose a suitable land plot. It must meet the following requirements:
- be convenient for the homeowner;
- be located near transport interchanges, have an entrance;
- be able to connect to communication networks;
- infrastructure facilities (schools, kindergartens, shops) should be located nearby.
To obtain a building permit, you must personally apply to the city or district BTI. In the department, you need to write an application according to the model and attach documents confirming the right to own land (a lease agreement, a document of sale, etc.) to it. In addition to legal documents, you will need:
- certificate of determination of the boundaries of the site;
- survey project;
- cadastral plan;
- project of the house and development of the site.

You may also need an estimate of the planned costs of construction. More precise information about the required documents can be obtained from the BTI and the Department of Architecture.
The obtained permit is valid for 10 years. During this period, you need to have time to put all plans into practice.
It is quite difficult to draw up a development project on your own, taking into account all the requirements of SNiPs, fire and sanitary rules, but you can try. It is necessary to draw a plan of the site, as well as adjacent sectors. Calculate all distances necessary to ensure fire safety.
Then divide your plot into sectors, decide where the garden part will be, where the house and outbuildings will be, make the necessary indents. If it does not work out, then it is better to contact special organizations involved in planning the development of the housing sector.
When starting building, you need to remember that on the land allocated for individual housing construction, you can only build private houses and outbuildings (greenhouses, garages, baths, sheds), and not commercial buildings. At the same time, it is necessary to comply with the fire and sanitary rules adopted in SNiPs, as well as take into account the characteristics of the sector being developed.